Cable marking makes it possible to identify the product, determine its characteristics and scope of application. Today, letters and numbers, colored shells, electronic markers, special tags and labels are used. Deciphering the markings of wires and cables will be discussed further.
Wire classification
Wires, depending on their purpose, are divided into:
- installation;
- installation;
- power.
Each of these types can be made of aluminum or copper, and also have a shell or not. At the same time, copper wires are stronger than aluminum wires and can withstand higher voltages, and therefore they are more popular and widespread.
A cable is a group of wires under a common insulating sheath. In turn, they are usually divided into:
- control - ensure the transmission of a control signal;
- power - used for electrical wiring;
- radio frequency - intended for radio engineering devices and communication;
- for control - used in automatic systems.
Naturally, when choosing a cable, it is necessary to take into account both the purpose and the cross-section of the wire (varies from 0.35 to 70 mm2), the number and material of the cores, as well as the quality of the protective sheath, which is reflected in the marking of each product.
Letter marking
Cable marking involves coding, which includes the designation of the core and sheath material, insulation, wire cross-section, type of protection and the presence of armor.
The first thing to begin with when decoding the markings is the alphanumeric inscriptions. According to GOST 16442-80, as well as TU 16.71-277-98, groups of letters are used to designate cables. So, if there is an “A” at the beginning, then the wires are aluminum, but if it is missing, the wires are copper. The second sign gives an idea of the type of cable. There are several options here:
- "P" - flat;
- “K” - control;
- "M" - installation;
- “Ш” or “П(У)” - installation;
- “MG” is an installation type with a flexible core.
The third letter (or group) allows you to determine the quality of the insulating material:
- "P" - polyethylene;
- “B” or “BP” - polyvinyl chloride;
- “P” - regular tires;
- "K" - cardboard;
- "ME" - enamel;
- “Ш” (“О”) – polyamide silk (silk braid);
- "C" - fiberglass;
- “N” or “NR” - nairite;
- "L" - varnish;
- “F” - seam insulation;
- “E” - shielded insulation;
- “G” - flexible core;
- "T" - support cable.
The last letters indicate the type of sheath (cover), the presence of armor and the filling of the cable:
- “A” – aluminum,
- “P” – polyethylene;
- “R” - rubber;
- “B” – polyvinyl chloride;
- “C” - lead;
- “K” - armor made of galvanized wire;
- “E” - copper wire screen;
- “Ps” - a shell made of self-extinguishing polyethylene;
- "NR" - rubber insulation and sheath;
- “LS” - with reduced smoke emission;
- “FR” - increased fire resistance;
- “M” - oil-filled cable;
- “B” - armor made of steel tapes;
- “G” - gas-filled cable without a protective layer;
- “Shv” - sheath made of polyvinyl chloride hose;
- “Shp” - polyethylene hose;
- "ng" - does not support combustion.
The numbers in the marking indicate the number of cores and their cross-section.
Let's give a few examples.
- ASB 7×2.5 is an aluminum 7-core cable with a cross-section of 2.5 mm 2, with armor and a lead sheath.
- The “ASG” marking indicates the presence of an aluminum core, paper insulation and a lead sheath without protective covers.
- AVVGng 3×4 is a 3-core aluminum cable with insulation and sheath made of polyvinyl chloride, without a protective cover and does not support combustion. Section of this cable is 4 mm 2.
In addition, some cables are provided with a specialized abbreviation. In such cases, additional groups of letters will indicate that the product is intended for:
- fire alarm - “KPSVV”;
- shielded for fire alarms - “KPSVEV”;
- special transmission systems in a shell - “KSPV”.
Color marking
In addition to alphanumeric designations and inscriptions, it is used color coding. In this case, the list of colors is regulated by GOST 28763. According to this document, each sheath color corresponds to a specific wire:
- blue means neutral wire;
- black – phase;
- yellow-green – grounding;
- yellow-green with blue marks - combined neutral and ground conductors.
Note that for the phase conductor, in accordance with the PUE, it is allowed to use brown color
More details about color coding can be found in the following table.
Thus, when purchasing a cable, you need to pay attention to the color marking, since it may not correspond to your requirements in reality, and therefore, difficulties will arise when installing the cable and its further maintenance. On the other hand, color marking in no way affects the quality of the product, and therefore, when using a cable with non-standard core colors, you should clearly determine which color will correspond to each specific conductor.
Tags for marking power and control wires
Tags are used to mark power and control wires. They are usually made of plastic or polypropylene, and are fixed at the cable inlet and outlet in cases of hidden wiring, as well as at the junction box. According to existing standards, cable marking tags come in four types:
- U-134.
- U-153.
- U-135.
- U-136.
In conclusion, we note that the marking of foreign-made cables differs significantly from domestic ones. As an example, here are just a few letter designations:
- N - compliance with VDE standard (Germany);
- Y - PVC insulation;
- 2Y - polyethylene insulation;
- 2X - cross-linked polyethylene insulation;
- E - three-core cable;
- S or C - copper screen;
- R - steel wire armor.
Obviously, the cable markings are very diverse, and it is quite difficult for the average person to understand them. Therefore, without special skills and experience, you should contact a specialist. The ideal option would be if the services of a cable laying technician include the purchase of all the necessary materials.
World manufacturers household appliances When assembling their equipment, they use color coding for the mounting wires. It represents the designation in electrics L and N. Thanks to a strictly defined color, the master can quickly determine which of the wires is phase, neutral or ground. This is important when connecting or disconnecting equipment from power.
Types of wires
When connecting electrical equipment and installing various systems, you cannot do without special conductors. They are made of aluminum or copper. These materials conduct electricity well.
Important! Aluminum wires must only be connected to aluminum wires. They are chemically active. If they are connected to copper, the current transmission circuit will quickly collapse. Aluminum wires are usually connected using nuts and bolts. Copper - through a terminal. It is worth considering that the latter type of conductors has a significant drawback - it quickly oxidizes when exposed to air.

Advice in case the current stops flowing at the site of oxidation: to restore power supply, the wire must be insulated from external influence using electrical tape.
Wire classification
The conductor consists of one uninsulated or one or more insulated conductors. The second type of conductors is covered with a special non-metallic sheath. This can be a winding with insulating tape or a braid made of fibrous raw materials. Bare wires do not have any protective coatings. They are used in the construction of power lines.
Based on the above, we conclude that the wires are:
- protected;
- unprotected;
- power;
- installation.
They must be used strictly for their intended purpose. The slightest deviation from operating requirements leads to a breakdown of the power supply network. As a result of the short circuit, fires occur.
Designations of phase, neutral and ground wires
When installing electrical networks for domestic and industrial purposes, insulated cables are used. They consist of many conductive wires. Each of them is painted in a corresponding color. The designations LO, L, N in electrics allow you to reduce the time for installation and, if necessary, repair work.
The electrical designation L and N described below fully complies with the requirements of GOST R 50462 and is used in electrical installations in which the voltage reaches 1000 V. They have Electrical equipment of all residential, administrative buildings, and commercial facilities. What color designations for phase L, zero, N and grounding must be observed when installing electrical networks? Let's figure it out.
Phase conductors
Online AC There are conductors that are energized. They are called phase wires. Translated from English language The term "phase" means "line", "active wire", or "live wire".
Human contact with a phase wire exposed from insulation can result in serious burns or even death. What does the designation L and N mean in electrical engineering? On electrical diagrams phase wires are marked with the Latin letter “L”, and in multi-core cables the insulation of the phase wire will be painted in one of the following colors:
- white;
- black;
- brown;
- red.
Recommendations! If for any reason an electrician doubts the veracity of the information displaying the color marking of the cable wires, a low-voltage tester must be used to determine which wire is live.

Neutral conductors
These electrical wires are divided into three categories:
- zero working conductors.
- neutral protective (ground) conductors.
- neutral conductors, combining protective and working functions.
What is the designation of wires in electrics L and N? Network neutral or zero working conductor in circuits electrical circuits denoted by the Latin letter “N”. The neutral conductors of the cables are colored as follows:
- blue color throughout its entire length without additional inclusions;
- blue along the entire length of the core without additional inclusions.
What do L, N and PE mean in electrical engineering? PE (N-RE) is a neutral protective conductor, which is painted with alternating lines of yellow and green along the entire length of the wire entering the cable.
The third category of neutral conductors (REN-wires), which combine working and protective functions, have a color designation in electrical engineering (L and N). The wires are painted blue, with ends and connections with yellow-green stripes.
The need to check the labeling
The designation LO, L, N in electrical engineering when installing electrical networks is an important detail. How can I check if the color coding is correct? To do this you need to use
To determine which conductor is phase and which is neutral using indicator screwdriver, you need to touch its tip to the uninsulated part of the wire. If the LED lights up, it means that a phase conductor has been touched. After touching the neutral wire with a screwdriver, there will be no glowing effect.
The importance of color marking of conductors and strict adherence to the rules of its use will significantly reduce the time of installation work and troubleshooting of electrical equipment, while ignoring these basic requirements results in a health risk.
Today, it is simply impossible to imagine installing electrical wiring in an apartment or private house using wires without colored insulation. Wire color coding- this is not a pursuit of fashion or a marketing ploy by a manufacturer who wants to lure a potential buyer with his colorful electrical products.
Differentiating electrical wires by color is an urgent need. Firstly, by the color scheme we can determine the purpose of each conductor located in a particular group of wires. Secondly, the likelihood of making a mistake during connection and connection is greatly reduced, and this will save the electrical wiring from short circuit and electric shock to humans.
The color of the wire insulation is not chosen arbitrarily. There is a single color standard, clearly stated in the PUE (electrical installation rules). It says that all wire and cable cores must be identified by color or alphanumeric designations.
With the adoption of a unified standard for the color designation of electrical conductors, their installation has become much easier. Each core has a specific purpose and is designated by a unique color: black, white, yellow-green, blue, etc.
Most often, the insulation of an electrical wire is painted in color scheme along its entire length. But it is also possible to use colored heat-shrinkable tubes (cambrics) or colored electrical tape at the ends of the cores and at connection points.
Let's consider what color markings of wires are used in single-phase, three-phase and DC.
Wire colors in single-phase wiring
IN electrical networks alternating current, multi-core wires with insulation of different colors are used, which greatly facilitates installation work and eliminates connection errors.
Let's find out what colors the conductors have in AC electrical installations with voltages up to 1000V and with solidly grounded neutral(most administrative buildings and all residential buildings).
Color of zero protective and zero working conductors
The neutral working conductor (N) should always be blue. The neutral protective conductor (PE) is painted in yellow-green longitudinal or transverse stripes. Wires with this color combination should only be used for their intended purpose!
The combined neutral working and neutral protective (PEN) wire is blue along the entire length of the conductor with yellow-green stripes at the ends. GOST also allows the opposite option - yellow-green stripes along the entire length with blue at the ends.
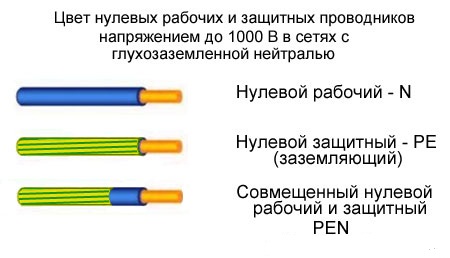
So, neutral wires by color:
Zero worker (N) - blue color;
. zero protective (PE) - yellow-green color;
. combined (PEN) - yellow-green with blue marks at the ends (or vice versa).
Phase wire color
 Phase wires in electrical wiring, according to the recommendations of the PUE, should have the following colors: black, brown, red, gray, purple, pink, white, orange and turquoise.
Phase wires in electrical wiring, according to the recommendations of the PUE, should have the following colors: black, brown, red, gray, purple, pink, white, orange and turquoise.
We know that a single-phase one is created by branching from a three-phase one. In this case, the phase conductor of a single-phase circuit must necessarily match the color of the phase conductor of a three-phase circuit with which it is connected.
In no case should the colors of the phase conductors coincide with the colors of the neutral and grounding conductors (N, PE, PEN).
When using a stranded wire (cable) with single-color markings, colored marks are placed at the ends of the wires (after testing). For this, colored heat-shrinkable tube (cambric) or colored electrical tape is used.
Conductor color in variable three-phase network
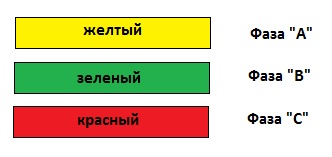
In three-phase networks, buses and high-voltage inputs of transformers at and substations must have the following color: phase “A” - yellow, phase “B” - green, phase “C” - red.
Color of wires in DC network (+ and -)
As we know, a DC circuit uses only two wires. There is no phase or neutral conductor, but only positive (+) and negative (-) wires.
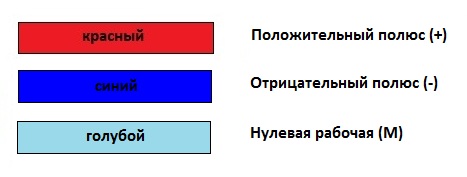
According to the standards, electrical conductors of a positive charge (+) are painted red, and conductors of a negative charge (-) are painted blue. The middle conductor (M) is indicated in blue.
Recommended articles:
Winding electrical wires
IN modern life Marking wires by color is not an advertising ploy by the manufacturer to stand out from others. This is a necessity and requirement, without which fast and high-quality installation of electrical wiring is impossible. How does this color help?
- quick identification of wire purpose (phase, neutral or ground)
- reducing the number of erroneous connections during the installation process
- no need to test the wire for phasing
Manufacturers choose conductor colors not according to their own wishes, but according to the rules. Moreover, not only a color, but also a numerical and alphabetic designation can be applied to the conductor. 
The color is applied along the entire length of the core insulation. But in some areas you can also use multi-colored cambrics for heat shrink. They are mainly widely used in cable terminations. 
Coloring for 220V and 380V single-phase and three-phase voltage
In a three-phase network, wires and buses were previously colored as follows:
Yellow color
Green color
Red color
To make it easier to remember the order of colors, electricians used the abbreviation ZH-Z-K. 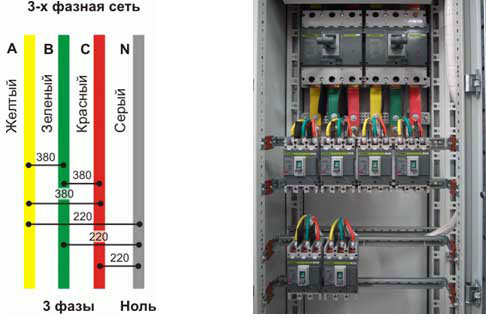
From 01/01/2011, new standards were introduced in accordance with GOST R 50462-2009 ():
Brown
Now it's time to switch to abbreviations - K-H-S! Subjectively speaking, this marking is inferior in clarity to the previous color scheme Zh-Z-K. 
Imagine that there is poor lighting in the control room or room, dust on the wires? Which do you think your eye is better at distinguishing between yellow and green or brown and black? The rules in this case stipulate the need for letter designation and marking of the cores, in addition to color.
Letter designation of wires
What should be the letter designation of wires according to GOST is presented in the following tables: 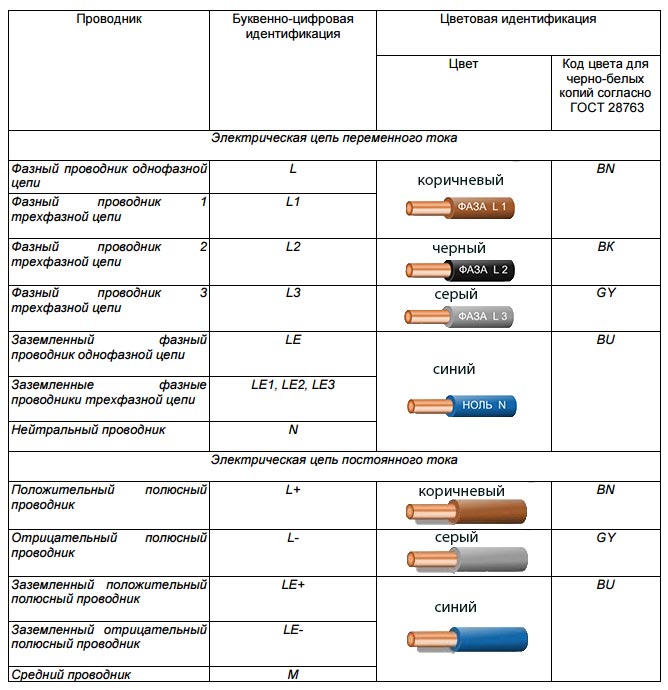
 It is best to apply these letters using special tag rings.
It is best to apply these letters using special tag rings. 
They are a PVC tube, pre-cut, with letters and numbers printed on it. 
Mark phase conductors yellow or green According to the new rules it is prohibited. Precisely because of their similarity with the yellow-green grounding conductor.
It is also worth highlighting that brown– exactly phase A or L1 (simply L in a single-phase 220V network), and black – phase B or L2. When you conduct wiring for yourself, you may unwittingly miss this moment. But if electrical work is being done at an industrial facility, then you will be required to strictly comply international standard and correct phasing.
White color is the cheapest option when making core insulation, as it does not require the use of dyes. Therefore, it is most often used by manufacturers of cheap cable brands. There are no special labeling guidelines for this color.
Coloring in a DC network
DC networks use 3 buses. The usual zero and phase are missing here. There is a positive conductor or bus (with a plus sign) and a negative conductor (with a minus sign). According to the old rules, the positive tire should be red, the negative tire should be blue. Zero operating bus – blue. 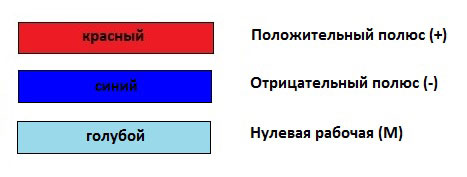
According to new standards from 01/01/2011:
Plus
Brown color
Minus
Gray color
Middle conductor
Blue color
Errors and color options for phase, neutral and ground wires
The issue of marking wires by color becomes acute when the wiring is installed by one electrician and then serviced by another. If you follow all the color rules, you will save a lot of time and money on troubleshooting.
Unfortunately, in old Soviet wiring, most of the conductors are single-colored and there is no way to do this without a probe or multimeter. 
If color marking exists and is observed, then the neutral and protective wires should be:
Neutral wire N should be blue.
Zero protective PE – yellow-green.
The conductor combining the protective zero and the working zero PEN is yellow-green along the entire length of the wire, but at the end at the junction it is blue. 
When coloring phase wires, the manufacturer is given a choice from a variety of color options. Here are the main ones: ![]()
At the design stage of any object, the working drawings must include cable markings and an explanation of this marking.
In addition to this, there are tags that are attached to each product.
Industrial production, energy, communications and other industries cannot function without the use of cables and wires.
Over the past decades, the product range has increased. SIP and other types of wires have appeared on the market.
In order for interested parties to navigate this diversity, a special table has been developed.
The decoding table shows the characteristics of each product, which must comply with GOST.
A cable is a complex technical product. Factory markings are applied to its outer surface and represent a specific code.
In accordance with current legislation, this cipher has a certain structure.
Every specialist can easily determine technical specifications cables, which include:
- core material;
- cross-sectional area;
- operating voltage;
- cable purpose;
- insulation material;
- product features.
In this context, it should be noted that when performing electrical installation work, cable products, cords and wires are used.
When installing power lines and other communications using SIP wire, tags with printed information are attached to it.
Types of cable products
You need to clearly understand the differences between a wire and a cord and a cord and a cable. Marking of wires and cables is carried out according to one GOST.
A wire is a product made from one or more cores twisted together. Products are produced with or without applied insulation.
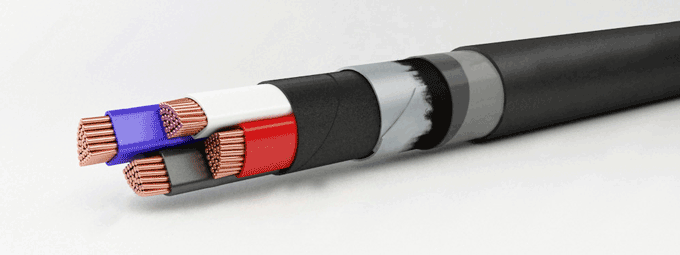
Widely used in the production of electric motors, generators and other types of industrial products.
The cord is made by twisting several strands that are highly elastic.
The main scope of application of a flexible cord is connecting to the network of various electrical appliances household and industrial use.
Deciphering the flexible wire markings allows you to accurately determine the scope of application of the product. The range of manufactured cables is divided into the following groups:
- power;
- control;
- radio frequency;
- management;
- communications.
For each type of product, GOST has been developed, which regulates the technical characteristics and operating conditions of each product.
Wire type VVG is not used in communication networks. In the same way, the use of the coaxial standard in power supply systems is prohibited.
According to building codes and regulations, each wire laid in a tray must have tags that are located every 50 meters.
Power
This type of product includes VVG and SIP wires. They are used in power, lighting and household circuits.

GOST prescribes that wiring in domestic premises should be carried out with a cable made of copper conductors.
For special conditions, armored products are laid in mines and underground galleries.
Tests
These products are used in systems remote control, for powering electrical devices.
The number of conductors, according to GOST, varies from 4 to 37.

Labels with the prescribed information are attached to both ends of the cable.
Radio frequency
Cables are produced for transmitting high-frequency signals from one electronic device to another.
Coaxial type product.
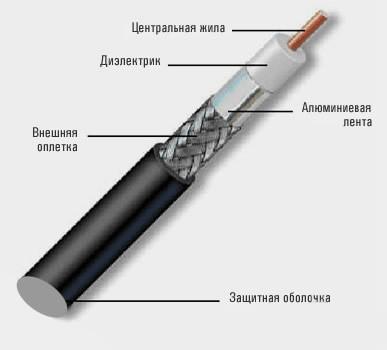
Copper inner wire.
Insulation – polyethylene.
On top of the insulation, a second conductor and a plastic protective sheath are applied.
Management
The products are used in remote control structures for various mechanisms.

Unlike the coaxial type, they have a number of current-carrying cores from 3 to 108.
Connections
A special type of cable is used to transmit information and communication signals between subscribers.
The number of copper cores is determined by the purpose of the cable.

The product is divided into two types - low-frequency and high-frequency.
Alphanumeric marking structure
Marking wires and cables in accordance with GOST allows you to quickly find the desired wire among similar products that have the same type and color.
At large industrial facilities, where the number of installed communications is in the thousands, tags are used.
The information printed on the surface of the product and on the tag contains data about its parameters and purpose.
An experienced installer just needs to look at the markings and find out the size of the cross-section of the cores; cross-sectional area, which ranges from 0.35 to 70 square meters. mm; the number of cores and the metal from which they are made.
SIP wires are made from aluminum billets. The VVG cable, according to the marking, is made of copper wire.
Cable marking according to GOST indicates data on the rated voltage for which this product is designed. The marking also contains information about the insulating material.
According to GOST, the list of such materials is strictly limited. Among the most well-known are rubber, paper, PVC and other plastics.
And one more important parameter, which is important when choosing a cable, is the material of the protective sheath. The outer shell is made of metal, plastic, rubber.
Tags with information about the purpose of the product are attached during the installation process. Decoding the markings on the cable, according to GOST, is inherently simple.
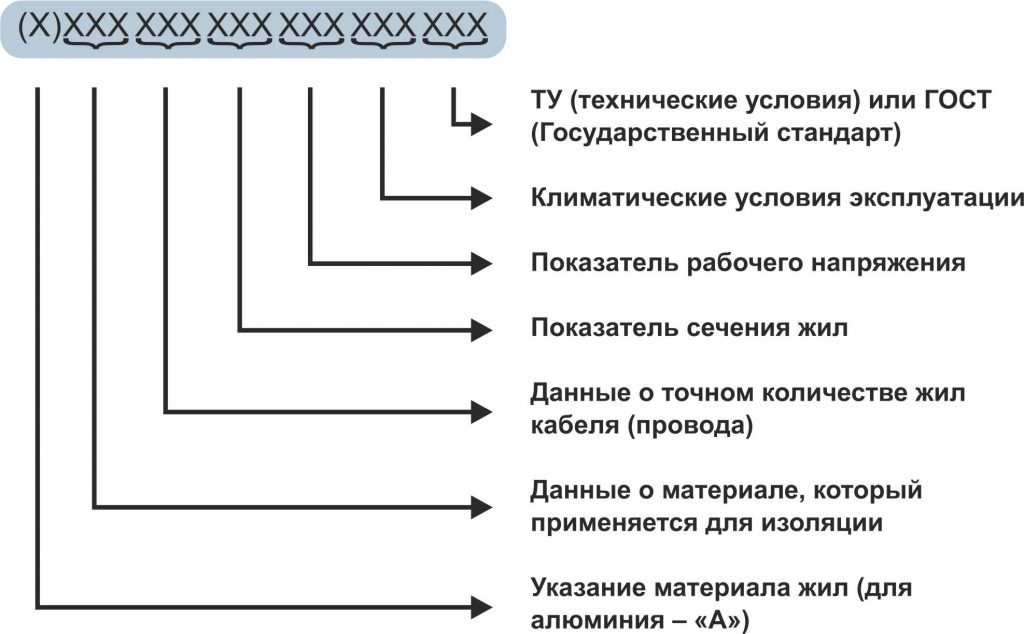
The initial letter in the marking code characterizes the metal from which the core is made. For aluminum conductors, the letter “A” is used. There are no letters for copper.
The second letter indicates the insulating material of the cable. "B" is vinyl or PVC. "R" - rubber. The third letter refers to the insulating material of the core.
The same materials are used here, vinyl and rubber.
The fourth letter characterizes the cable design. “A” indicates that the wire is covered with an asphalt coating. "B" - armored with metal. “G” - has no protective cover or, as installers say, naked.
The first number indicates the number of cores. The second is about the cross-sectional area. The third is about the operating voltage for which the cable is designed.
If you quote the marking VVG -3x1.5-380, then everything will be clear to a specialist. Since the letter “A” is missing at the beginning, it means the vein is copper.
The letter “B” indicates that the cable insulation is vinyl. Just like the vein, this is indicated by the second “B”.
The letter “G” means that there is no protective cover. The first number is 3 wires. The second number is the wire cross-section of 1.5 square meters. mm. And the last number is the operating voltage 380 V.
This is how the cable marking is deciphered according to GOST.
Designation options
Marking is the process of applying a code, color marks and other elements to the surface of a product.
SIP cable is used when installing power lines and all designations are applied to it in standard ways, like on VVG or any other. For all types of marking there is a corresponding GOST.
The manufacturer produces color, letter or other markings. This allows consumers to differentiate welding equipment products from coaxial cable.
When installing communication systems and optical fiber, the ends are marked. Identification tags are attached to the connections and contacts.
A schematic table is presented below:

IN recent years For optical or coaxial cables, electronic markers are used, which is not done for welding equipment. New communication technologies are driving improved labeling methods.
Color or symbol markings do not lose their significance either for welding equipment or for coaxial cable.
It continues to be used to refer to:
- SIP wires;
- coaxial cable.
At the same time, marking according to GOST power cables remains traditional. The color structure has long become familiar, and there is no reason to change it.
The color marking of the sheaths in which the wires are enclosed (including for welding equipment) indicates the following:
- “earth” - yellow-green;
- "zero" - blue;
- “phase” - brown, gray, red.
Manufacturers of VVG cables, SIP wires and other types also adhere to this optical range.
Communication cables, which are used in various segments of telecommunications, contain a large number of cores.
In order to quickly find the desired ending, they have to be marked at the installation stage. Conventional tags are not suitable for this.
Today, other methods are used for these purposes. GOST allows manual method markings.
Marking equipment
Manual or artisanal marking is done with permanent markers. This technology is used by small and medium-sized businesses.
For power cables of the VVG type, just like for communication cables, this method will be used for a long time. At the same time, the production of special marking equipment has been established.
Many years of experience show that the time-tested tag should not be abandoned just yet. New equipment must be tested in real conditions and on large volumes of work.

SIP wires can be marked in the old way, but you need to take a closer look at the electronic marker.
More than 50 years ago, devices for cold and hot stamping began to be used. This equipment is still in use, although it is already completely obsolete.
Marking according to GOST for VVG type cables and SIP wires is carried out with high quality. In this context, it should be noted that modern methods allow you to get results faster and cheaper.
Any marking is characterized by its service life, the material from which it is made and other characteristics.
Among the latter are resistance to moisture, high temperatures, and mechanical contacts.
The method of attaching the marking element is of great importance. You can fix it in the right place using welding equipment, glue or clips.
In addition to applying a code to the SIP cable, you can use various adhesive tapes. GOST allows this action on a par with the use of welding equipment.
Modern marking equipment allows you to apply complex inscriptions and symbols on communication wires.
These designations may differ in font style, type and color of tape, and arrangement of symbols. The color palette of symbols can be very different.
Marking of power cables that are laid in underground communications can be done using an electronic marker.

In this case, no color or other marking is required. A passive electronic device, which is a marker, will allow you to determine the location of the cable, its beginning and end point.
The use of such markers allows you to reduce the time it takes to search for a gust, if this happens.
Using a special device called a marker finder, the desired point on the route is determined without opening the ground.
The VVG wire is highly reliable, but during operation and repair work it can be damaged.
To eliminate any malfunction in accordance with GOST or other regulatory document a very specific amount of time is allocated.
In order not to violate established norms and rules, you must initially carry out all work in accordance with technical specifications for welding and other types of equipment, including marking wires and other elements of electrical installations.
Then it was possible to decipher the cable markings for welding or other equipment quickly and effortlessly.