Many people, when they talk about such a thing as electrical power, mean some kind of force. However, even in the school physics course, knowledge was given that power and force are different concepts, although interrelated.
The very concept of “power” means a characteristic of a certain event. In this case, you can associate power with some object. Any physical impact can be called the action of force. Perfect work is the distance traveled with the help of an applied force. The work done by a force in a certain time will be equal to the power. Thus, power is a physical quantity equal to the ratio of the work done in a certain time by a certain force to this period of time.
However, we must not forget that power is also a measure of energy. Therefore, we can take into account the statement that this term can also be used to refer to the change in energy in a certain system (the rate of energy conversion).
Although the above terms and definitions relate more to mechanical energy, from all this we can derive the concept of “electrical power”. The product of current and voltage is called Since this concept depends equally on both voltage and current, we can say that the same electrical power is obtained both at a high current and a lower voltage, and at low currents. This property underlies the transmission electrical energy over long distances using power plants, substations, and step-down), switchgear and other electrical equipment.

Electrical power is divided into two main types: reactive and power - this is a characteristic of the transformation of electricity into other types of energy (heat, movement, light). Electrical power is measured in watts (W). In everyday life, such energy is usually measured in kilowatts, and at large power plants larger units are used - megawatts.
Reactive electrical power characterizes the electrical load in various devices. It is equal to the product of the voltage drop and the operating current and the sine of the phase displacement angle (phase shift) between the current and the voltage drop. Reactive power is measured in reactive volt-amperes (VAr).
Active power can be related to electrical power through a concept such as “cosine phi” - the phase difference between current and voltage. For most household appliances this cosine will be approximately 0.8. For heating devices it is often raised to virtually unity.

Electrical power is measured with a special device - a wattmeter. Such a device has two windings. The first is a thick wire, connected together with electricity consumers and records the change in current value. The second winding consists of a thinner wire and is connected in parallel to account for the voltage in the network. In power plants, the concept of “installed electrical capacity” is often used, which is the sum of all of only one type or type (for example, transformers, generators, motors).
Since everyone has many electrical appliances, you need to know their power consumption. This is useful for adjusting your electricity bills and so as not to overload your line from the meter. The maximum that a device can consume is called rated power. This indicator is indicated on the device itself or in its technical documents.
First way
In cases where the device does not use its maximum force, its load can be calculated independently. To do this you will need:
- Meter;
- Calipers;
- Tester.
Taking measurements
Before doing this, you need to study the device or its documents, as the rated voltage and power may be indicated there. When the device indicates that its consumed load is 200 W and the voltage is 220 V, then when connected to a regular 220 V network, the device consumption will be 200 W. If some parameter is not indicated, you need to connect the device to the network and using a tester you can find the current strength that flows through it and its operating voltage.
 To understand how to calculate the consumed load of an electrical appliance, you need to configure the tester to operate as an ammeter. It must be connected in series to the consumer. When the appliance used is operating at DC, you need to take into account its polarity when connecting. Readings are taken in terms of current strength, that is, in amperes. Then the tester switches to voltmeter mode and is connected in compliance with polarity, if the current is constant, parallel to the device. These readings will show volts.
To understand how to calculate the consumed load of an electrical appliance, you need to configure the tester to operate as an ammeter. It must be connected in series to the consumer. When the appliance used is operating at DC, you need to take into account its polarity when connecting. Readings are taken in terms of current strength, that is, in amperes. Then the tester switches to voltmeter mode and is connected in compliance with polarity, if the current is constant, parallel to the device. These readings will show volts.
To understand how many watts a consumer requires, you need to multiply the resulting voltage by the current.
![]()
When there is a parting resistance value, which is indicated in the documents or measured with an ohmmeter, the tester can perform the function of the latter. Then you need to measure the current and voltage. The power consumption indicator will be equal to the product of the square of the current and the resistance. When voltage is measured, the consumer load is defined as the ratio of the square of the voltage to the resistance of the device.
![]()
The consumption of electric motors is determined by the size of the core. You need to measure its diameter, length and rotation frequency, and also find out the pole division of the motor. Using a special table you can understand the constant load of the engine. The load consumption is calculated by multiplying the constant motor power by the squared core diameter, length and synchronous speed. The resulting data must be multiplied by.
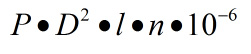
Second way
Since every home has many different appliances that are powered from outlets. Often, in winter time year, the power grid becomes overloaded. The consequence of this is that circuit breakers constantly knocks out, preventing the wires from heating up. In order to avoid such situations, it is necessary to connect through a stabilizer, and for this it is necessary to calculate the power consumption of all connected devices.
To do this you will need:
- Calculator;
- Phase meter;
- Instructions from the electrical appliance.
Taking measurements
You should know that electrical appliances have two types of power, such as active and reactive. They differ in that the active load consists of converting all the energy used into heat. This includes an electric kettle, iron, boiler, boiler and other appliances.
Other devices that run on electricity have a different power option. This includes electric motors. Full load and active load have a mutual relationship with each other. This is expressed in the formula Ra = cosφ*P, where P shows the total power, and PA is the active power. Cosφ is the power factor. It is determined by a phase meter, but sometimes this value is already indicated on the back of the case or in the device’s passport book. Knowing the power factor and the value of active power, you can calculate the total power of household electrical appliances.
The power consumption of household appliances can be high. The capabilities of a cottage's electrical network are laid down at the design stage, when its maximum power consumption is determined, which determines how many household appliances can operate simultaneously. When calculating power, the number of people living in the house, the power of each of the electrical receivers, their number, the nature of the load, and the type are taken into account. As explained by Vyacheslav Andreichenko, General Director of the DS Electro company, in the project, the plans show power supply routes for groups of power lines and electric lighting lines throughout all rooms of the house and area, broken down into groups and indicating all connected electricity consumers. The project involves calculating the lengths and cross-sections of cables depending on the installation methods, taking into account the consumed power of household equipment(which can be found in the power table of household appliances), as well as taking into account the length of the cable “by the voltage drop in the line”. Such calculations help to choose the correct cable cross-section, which will allow transmitting a given amount of power and providing the electrical receiver with the required voltage of 220/380 V. Proper design guarantees that internal and external electrical networks will be reliable and safe in operation. During the design, you can model the network and take into account all possible nuances, and subsequently the owner will save on installation.
The electrical part project must be started after architectural, design, landscape projects, engineering development (heating, water supply, ventilation, air conditioning), control and automation system design. Based on these data, it is possible to include in the project a wire of the required cross-section that will withstand the effects of currents flowing through it, and place sockets directly next to the devices so as not to clutter the interior with extension cords and tees. Modern household appliances, that is, the power of household appliances, consumes a lot of power - up to 5 kW. This should definitely be taken into account both when laying electrical wiring and when choosing sockets. The electricity meter and circuit breakers must also be designed for such a load. You can check whether the electrical equipment at home corresponds to the consumed currents yourself, using the formula:
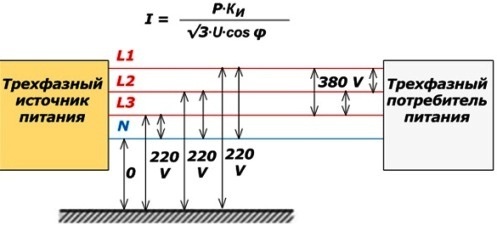
P=UxI, where P - device power, U=220 V - voltage in the socket, I - power consumption of household appliances. Knowing power of household equipment(indicated in the data sheet), the current can be determined. which will flow in the circuit. On sockets, meters, and machines there is a designation indicating the maximum current they are designed for. All household appliances operate from single-phase network, however, they can also operate on three-phase power. Experts recommend taking people into the house three-phase network: for the same starting costs it is more reliable.
The power table of household appliances, that is, the power of electrical appliances, is given above.
Safety All electrical appliances, the power consumption of household appliances, as well as the electrical network as a whole, carry the risk of damage electric shock, the occurrence of a fire. Therefore, the issue of ensuring security must be treated extremely responsibly.
All electrical appliances, the power consumption of household appliances, as well as the electrical network as a whole, carry the risk of damage electric shock, the occurrence of a fire. Therefore, the issue of ensuring security must be treated extremely responsibly.
Grounding. Electrical network at home must be grounded. According to the requirements of current standards, three wires are laid for a single-phase network, and five wires for a three-phase network. Without exception, all sockets and electrical receivers, including lighting, are grounded. Fast-rotating parts (a compressor in a refrigerator, a motor in a washing machine or dryer) are a source of static electricity due to friction. His blows are life-threatening. If the rotating part is grounded, the static charge will “drain” into the ground and the danger of electric shock can be avoided. When installing equipment in a room with a metal, concrete or other conductive floor, always remember about the so-called step electricity.
Spark protection. When using powerful devices, it is necessary to avoid sparks at the connection point. To do this, you must, firstly, use high-quality sockets. The plug inserted into the socket should not wobble or fall out easily. Secondly, an electrical appliance should only be plugged into the outlet when its switch is in the “OFF” position.
Overload protection. Often, electrical wiring around the house is carried out in a fan-type manner, namely: one power cable extends from the meter to the entire house and then, through distribution boxes, it is branched out into rooms. In this case, the wire of the same cross-section is used everywhere. The network can withstand the simultaneous activation of no more than two powerful devices in one room. If you plug it in at the same time, for example, into one outlet washing machine, in another - a kettle, in a third - an iron, and in a fourth - a microwave, this can lead to overheating of the equipment and even a fire.
Automatic devices protection. The meter must have automatic protection devices installed. If the permissible load is exceeded (many devices are turned on at the same time), they automatically turn off the entire network. Also, the machines operate at the moment short circuit- because too much current begins to flow. However, a current of 0.1 A is enough to kill a person. Of course, none of the “machine guns” will work from such a current. Therefore, to protect against leakage of small currents, it would be useful to install a device in the electrical panel protective shutdown(RCD). This device compares the currents flowing through the phase (to the electrical appliance) and neutral (from the device) wires, and turns off the circuit if the currents differ even by as small an amount as 0.1 A.
About the protection of electrical appliances
General Director of AS ELEKTRO
Low-current devices are very sensitive to distortions in the electrical network, microprocessor technology. Therefore, it is recommended to power computers, alarm systems, and electronics additionally from an uninterruptible power supply (UPS). It removes interference, stabilizes the voltage to the desired level and makes the voltage waveform sinusoidal without distortion. And due to the energy accumulated in the batteries, the uninterruptible power supply will be able to supply household electrical appliances with energy for a certain time if the voltage disappears. Of course, it will not be enough for long-term operation, but it is quite capable of covering the time until the generator starts up. If there are more than 2-3 consumers in need of a UPS, then instead of several devices it is more advisable to purchase one powerful UPS and install it in the place where electricity is distributed - near the electrical panel.
Network without interference
Voltage surges, pulse and switching noise are common in the domestic power grid. This leads to malfunctions of household electrical appliances, the blocks and modules of which are sensitive to voltage changes. The tolerance for differences is +10%...-15%, that is, from 187 V to 240 V. But in networks country houses the voltage can drop below 180 V and rise to 250 V. A breakdown of the device that occurs as a result of these influences will have to be corrected by the consumer at his own expense, even if the device is under warranty, because warranty repairs of equipment are carried out if the equipment malfunction occurred due to the fault of the manufacturer. And voltage surges are regarded as external influence, which is in no way the manufacturer’s fault. To minimize the impact of possible voltage surges, failures and interference, special equipment is used. To protect devices, it is recommended to use AC voltage stabilizers. In this case, it is worth considering the load power for which the stabilizer is designed, and not using household appliances with higher power consumption. To protect against an overvoltage pulse that occurs during a direct or remote lightning strike, it is necessary to equip internal lightning protection (by creating protective zones along the path of penetration of the overvoltage pulse, at each transition of the zones to limit the potential, a surge protection device is installed - a lightning surge arrester).
About electrical network design 
Architect of the PROJECT SALES CENTER
Standard project document package country house includes the engineering part, which shows wiring diagrams for in-house electrical networks, calculations device power, necessary electrical equipment, etc. The set of the most commonly used household electrical appliances is standard, which makes it possible to average out the probable load on the electrical network and the required power. For example, for a cottage with an area of 200-300 m2 without an electric boiler, about 20-24 kW of electricity will be required for heating. If the engineering part is in standard project is missing, it definitely needs to be developed, which is what they are doing in our center. The price of the issue starts from 1.5 dollars per 1 m 2 of the total area of the house. Electrical equipment at home - enough complex system. In order to feel safe, you need not to deviate from design decisions, because in the event of a breakdown, the project will help determine the cause and not destroy walls and ceilings in search of leaky wires, but make local repairs.
There wasn't enough power
The project has been approved, the house has been built, all communications have been completed, but the owner’s energy consumption plans have changed, and the power of the existing network is not enough. This scenario is not uncommon. There are several ways to solve the problem. The traditional method is to obtain permission from the regional energy supply organization to connect additional power. This scheme has a number of disadvantages; The local power grid may not have reserves or purchasing additional kilowatts may be expensive. A more practical way is to install an autonomous power supply. For example, diesel generators. Or use alternative sources energy - solar panels, wind stations. Such equipment is effective in our latitudes and allows you to create an independent home energy system that provides more than 3 kW of electricity.
An example from the life of new settlers
A young family with two children (4.5 years and 5 months) made an exchange and moved into a three-room apartment in a nine-story building built in the 80s from reinforced concrete panels with an elevator.
The electrical equipment of the apartment is made without a common grounding circuit and PE conductor. An introductory switchboard is installed at each entrance. From him power cables disperse along the floor panels. On each floor there are 4 apartments from two blocks; right and left with a common corridor. It contains housing panels that are powered by 2.5 mm2 “aluminum noodles”. The same wires are used for all electrical wiring in the rooms.
The new owner is a home craftsman who can not only hammer a nail, but also beautifully lay expensive tiles, repair plumbing, connect a washing machine/dishwasher, find faults in the phone and computer, and troubleshoot problems. software. But he is not an electrician, although he has repeatedly changed sockets and switches.
When checking the electrical wiring, the owner with a table lamp went through all the sockets and made sure they were in good working order. And I checked the lighting bulbs from the switches: they worked. He calmed down and got busy decorative finishing premises, and the problems began later.
In the fall, before the heating season began, heating was required in the children's room. We turned on an oil radiator with a power of 2 kW. At this time the washing machine and dishwasher, two televisions, a refrigerator with a freezer, a computer, lighting, a radiotelephone and several low-power consumers.
The smell of burnt electrical insulation appeared in the rooms. It came especially strongly from the common corridor from the apartment panel. I had to turn off the power supply from the apartment and figure it out: the overall picture from the electrician’s point of view looked depressing.
In the hallway, bathroom and living room there is a suspended ceiling made of plasterboard sheets, blocking access to distribution boxes. The bedroom and children's room are covered with expensive ones decorative wallpaper, and the junction boxes are not only hidden under them, but also beautifully plastered. Their approximate location had to be clarified with the neighbors living on the ground floor. Expensive tiles on the walls and permanent fabric suspended ceiling completely block access to the wiring in the kitchen.
I had to turn to electricians and technical reference books to analyze the situation. The apartment's aluminum wires were installed under the rated current load created by consumers thirty years ago. In addition, they have already served a decent amount of time:
aluminum was subjected to bending, stretching, crimping with screws, and in places of deformation its cross-section decreased;
polyvinyl chloride insulation was rubbed when pulled through the cavities reinforced concrete structures and experienced excessive heating from excessive currents during operation.
The most critical place turned out to be: where the neutral conductors were assembled. For these purposes, a two-part mounting platform was used. The first half received zero from the floor panel, and the second half collected all the other wires.
Between the platforms there was a jumper made of the same aluminum wire. The entire load of the apartment passed through it, like the incoming wire. The metal survived, but the insulation burned out over more than 2/3 of the length, starting from the first platform: the miscellaneous effects created by the screw clamps had an effect.
The insulation of the wire from the floor panel also began to melt, but not so intensely. The fire did not have time to occur - the electricity was turned off in time and the wires were allowed to cool.
Currently in this apartment:
the defective jumper was replaced with a copper one capable of withstanding heavy loads;
The new owners were explained the rules for using electrical appliances and their attention was drawn to the inadmissibility of simultaneously turning on powerful electricity consumers.
After a long conversation, the home master:
has seriously taken up the study of electrical engineering and electrical installation rules: he plans to replace the electrical wiring with a more powerful one using a new circuit with a PE conductor and is collecting money for the upcoming work;
contacted the housing and communal services regarding the transfer of the building to the power supply scheme according to the TN-C-S system, but was not satisfied with the answer that this work was still planned: he was looking for alternative options for the apartment located on the fourth floor.
Rules for choosing electrical wiring
To avoid such mistakes, for the safe use of electricity, you need to know the rules for choosing electrical wiring. It is designed to withstand long-term current loads that arise when connecting consumers.
The more devices are plugged into sockets, the higher the load on the electrical circuit. In each specific case, this value changes, but the maximum value is used to select the metal and wire cross-section.
In order to determine the maximum power consumption, it is recommended to make a table for all electrical receivers. Information should be taken from technical documentation or nameplates located on the device housing.
As an example, the table might look like this (although the numerical values may vary).
| Name of electrical device | Power in watts |
| Fridge | 300 |
| LCD TV | 140 |
| Ordinary vacuum cleaner | 900 |
| Vacuum cleaner washing | 2000 |
| Electric heated floor | 1100 per 10 sq.m. |
| Boiler | 2000-10000 |
| Electric stove | 1000 |
| Desktop computer | 400-500 |
| Laptop | 60 |
| Washing machine | 2500 |
| Dishwasher | 2500 |
| Incandescent light bulb | 60-100 (multiply by quantity) |
| Energy saving light bulb | 10-15 (multiply by quantity) |
| Electric kettle | 1000 |
| Multicooker | 1000 |
| Microwave oven | 2000 |
| Iron | 1700 |
| Electric drill | 400-1500 |
| Hairdryer | 600-2000 |
The list can be continued, but it will not be possible to provide for all possible purchases. Therefore, they make a small reserve of power, although it should be understood that all of the listed devices do not work at the same time.
The final information is summarized, but taking into account the creation of consumption groups by room. The results are entered into the prepared table.
Based on the calculations, a hierarchy is created electrical diagram apartments, in which not only wires are included, but also are selected taking into account the principle of selectivity protective devices, control devices, automation.
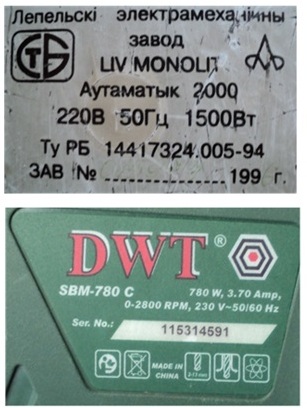
To determine the current load in the wire of each group, calculations are carried out using the formulas shown in the figure. For single-phase 220 V and three-phase 380 V circuits they differ by 1.732.
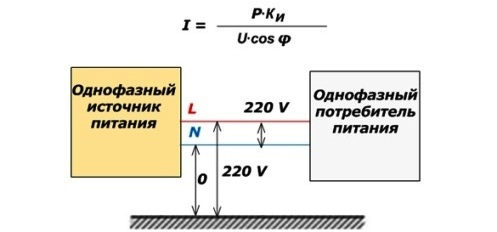
In these formulas, the index “P” indicates the resulting power of electrical appliances for each group with a network voltage of 220 or 380 volts
The coefficient of simultaneous operation “CI” approximately takes into account the part of the disconnected devices, and cos φ with such an approximate estimate can be equated to unity: assuming that only the active component of power is consumed. We neglect inductive and capacitive loads, as well as transient processes during switching.
After determining the current values, you should refer to the PUE tables to select the material and cross-section of the conductor. They take into account operating conditions that create additional cooling/heating of the metal.
Table for selecting wire and cable cores based on current and transmitted power (click on the picture to enlarge):
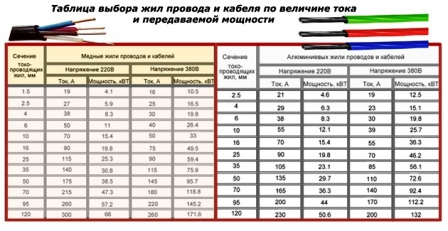
It is likely that the current calculated from the power of consumers will not coincide with table value. In this case, you should choose the larger of the two options in terms of value and select a section based on it.
Installation errors
Working with electrical wires, some electricians commit serious violations of existing rules:
the metal cores are often excessively compressed, scratches and cuts are made with a fitter’s knife, which are difficult to notice with the eye, but over time they lead to a break
the insulation is subject to abrasion by drawing, cutting, or exposure to solar radiation.
Influence sun rays for polyvinyl chloride insulation of electrical wires
Cables and wires can work reliably and for a long time: several decades if the technology is followed. But the picture below shows the effect of solar radiation on a wire that worked outdoors without any protection for only 5 years. You cannot create such conditions for electrical appliances.
Concluding the article, I would like to turn to experienced electricians with a request: supplement the material with your recommendations from practical work. This will help the home handyman who is interested in replacing the wiring in his apartment to perform such work more efficiently.