24/11/2008 17:04:54
Every schoolchild knows that combustion is special case oxidation process involving oxygen. In order for there to be fire and flame, air and the oxygen contained in it are necessary. The operation of an atmospheric boiler in this sense is no exception. When burning gas, any boiler, like a vacuum cleaner, absorbs air, which is then thrown into the chimney in the form of various oxides. For each boiler, the documentation indicates the volume of air consumed. The more powerful the boiler, the more air it consumes.
Often in private construction this fact is not given any importance. But in vain. A running boiler sucks air out of the house, creating a vacuum. This in itself is not scary if the walls of the house or window openings contain a sufficient number of cracks through which air from the street enters. However, recently, with the use of airtight plasters and modern window systems, houses are becoming impenetrable to the flow of air from outside. But the laws of physics cannot be canceled. During the heating season, a vacuum will be created in the house and the air from outside will tend to inward. In sealed houses, there is only one way for outside air to enter - ventilation ducts (hoods), which are usually located in bathrooms and kitchens. If the vacuum created by the boiler is greater than the resistance ventilation duct, the so-called reverse draft will appear from the hood. All odors that seem to be escaping through the ventilation ducts will not only remain in the room, but will also actively spread throughout the house along with the air entering from the street.
There is only one solution to this problem - forced ventilation. It can be common for the whole house or directly in the boiler room. From the point of view of ventilation science, it is extremely undesirable to make an influx only into the boiler room, since in the event of an accident there is a possibility of gas spreading to the entire house. In theory, the boiler room should only have hoods. However, gas services do not prohibit installing supply valves in boiler rooms. A general ventilation system is usually expensive and complex system, therefore the cheapest and in an efficient way ensure the flow of air - a supply valve directly into the boiler room or in the immediate vicinity of it. There are special valves with a special design, but they often make, simply put, a hole in the wall with a diameter of 100-150 mm. This is more than enough for the normal functioning of a medium-power boiler (20-30 kW). A sewer or ventilation pipe can be inserted into the hole made. Cover the outside of the pipe with a net to prevent leaves and insects, and place a simple one inside check valve. The cost of such a solution is minimal, and the efficiency is very high. Practice has shown that in winter the supply valve does not freeze. Despite the low temperature outside, the air temperature in the boiler room is slightly lower than in the general house.
Sometimes the diameter or location of the supply valve does not allow enough air to pass through to compensate for the air flow of the boiler. In this case, it is advisable to use the simplest fans, selecting the required air flow rate 15% -30% more than the flow rate of the boiler. Part of the fan power will be spent on overcoming the resistance of the valve, mesh, filter, air duct (if any). Partial air must escape through a natural ventilation duct, which is mandatory in boiler rooms. Significant air pressure through the supply valve in the boiler room cannot be done! It also makes sense to turn on the fan automatically when the boiler is operating for the same purpose - so as not to create excess pressure in the boiler room.
2014-01-08 14:09:50 | Yuri
Now they sell special pipes for gas boilers, a pipe in a pipe. One brings in cold air, the other removes smoke.
2013-11-24 09:59:57 | Andrey_B
Vladimir, if the draft is overturned, it means there is insufficient air flow in the house, that is, in this way (by reverse draft) the system balances the balance between exhaust and supply.
1. If there are sources of powerful air outflow, for example, a boiler, ensure a sufficient amount of air inflow. Typically, the boiler's air consumption standards are indicated in its documentation.
2. Calculate debit for ventilation ducts. And if it is very large, but there is no inflow, then either cover/close the ventilation ducts, or provide additional inflow.
3. After eliminating the imbalance, where reverse draft has formed, it may be necessary to warm up the ventilation duct so that it starts working for exhaust again.
2013-11-23 10:42:36 | Vladimir
I had a pull over in the bathroom. It’s impossible to wash - it’s cold in the bathroom. what to do?
2011-11-27 11:16:56 | Andrey_B
Alexander, do you mean forced ventilation?
The easiest way is a hole in the wall. For natural inflow, the hole must have a diameter larger than the diameter of the chimney. When installing a fan, the diameter of the hole can be made smaller. I also recommend installing a filter.
2011-11-26 22:46:49 | Alexander
boiler with a turbo hood, how can it be easier to make ventilation if there is a vent. no channels?
2011-08-16 08:51:41 | Andrey_B
Tim, the simplest supply valve is located only in the boiler room.
At the moment, the centralized ventilation system of the house is not running. If you supply air to living spaces, of course it will be necessary to provide heating.
2011-08-15 21:35:49 | Tim
“The stronger the frost, the higher the temperature of the coolant, the hotter it is in the boiler room.”
Andrey, did I understand correctly - you have one air supply for both the boiler room and the residential premises? Therefore, cold air is supplied to living spaces? Is there any discomfort in severe frosts?
2011-08-11 23:38:46 | Andrey_B
Tim, at the moment there is no provision for heating the supply air. In winter, the boiler room does not drop below +26 +28. The stronger the frost, the higher the temperature of the coolant, the hotter it is in the boiler room. The supply air is heated automatically. What you really need is a filter. The boiler room is dusty. The most surprising thing is that even in winter there is a lot of dust, or rather suspended matter such as fine sand. This is unlikely to be a problem for the boiler, but it lies in a thick layer on all pipes and fittings.
2011-08-11 17:14:45 | Tim
Question about ventilation of residential premises. Andrey, do you turn on the outside air heating in severe frosts? Or are you simply significantly reducing air exchange?
Page 1
Ventilation of boiler rooms is most often done natural with the influx of clean air through louvered grilles located in the walls of the rooms behind the boilers, and with exhaust through exhaust shafts or pipes located above the boilers in the ceiling of the boiler room. If natural ventilation is not possible, an artificial ventilation system is constructed using a fan. Exhaust fans and their electric motors installed in premises are explosion-proof to avoid an explosion from a spark in the event of the formation of a gas-air mixture. Explosion safety of the fan is achieved by covering the inner walls of the fan casing (stator) with aluminum or copper sheets or by copper plating them in another way. In this case, spark formation in the fan cannot occur.
Ventilation of boiler rooms is most often done natural with the influx of clean air through louvered grilles located in the walls of the rooms behind the boilers, and with exhaust through exhaust shafts or pipes located above the boilers in the boiler room ceiling. If natural ventilation is not possible, an artificial ventilation system is constructed using a fan. Exhaust fans and their electric motors installed in premises are explosion-proof to avoid an explosion from a spark in the event of the formation of a gas-air mixture. Explosion safety of the fan is achieved by covering the inner walls of the fan casing (stator) with aluminum or copper sheets or copper plating in another way. In this case, spark formation in the fan cannot occur.
Ventilation of boiler rooms is most often done natural with the influx of clean air through louvered grilles located in the walls of the rooms behind the boilers, and with exhaust through exhaust shafts or pipes located above the boilers in the boiler room ceiling. If natural ventilation is not possible, an artificial ventilation system is constructed using a fan. Exhaust fans and their electric motors installed in premises are explosion-proof to avoid an explosion from a spark in the event of the formation of a gas-air mixture.
Ventilation of boiler rooms must provide at least three times the air exchange without taking into account the air required for gas combustion. The air supply is carried out behind the boilers, and the exhaust is carried out from the upper zone. Gas burners of boilers and furnaces, manufactured according to current standards, must ensure combustion stability within the limits of regulation of the permissible thermal load of the unit. There are inspection holes on the front panel or firebox doors of the units through which the burners are ignited and their operation is monitored. An explosive gas-air mixture can accumulate in fireboxes, hogs and flues; to prevent the accumulation of this mixture, special holes with a diameter of at least 50 mm are installed in the boiler valves.
A feature of the ventilation of boiler rooms built into buildings is the need to ensure at least three air changes per hour. The volume of air entering the boiler furnaces for gas combustion is taken into account additionally. When determining the multiplicity, the volume of the room is taken minus the volume occupied by the equipment. The air supply in these boiler rooms should, as a rule, be carried out behind the boilers, and the removal should be from the upper zone of the room. This allows cold supply air to be supplied to an area where there is no maintenance personnel, and the gas collected in the air to be removed. upper parts premises as a result of possible leaks.
The mechanical ventilation method for a boiler room is carried out by installing 4 - 5 axial fans of type MC No. 8 in special supply cabins at a level of 6 - 1 m from the floor level. The supply air is usually not heated. However, with large quantities of removed air, the excess heat in the boiler room may not be enough to heat the supply air coming from outside.
The boiler room ventilation system diagram is very simple. During operation of the boilers, air from the room is removed through combustion devices, and supply air is supplied to cold period years through openings with fixed blinds or window transoms of the upper tier. Deflectors are installed on the ceiling of the boiler room, the performance of which is calculated for at least three times the air exchange in the boiler room. In the transitional and warm seasons, when the amount of air removed through the combustion devices is not enough to ensure proper exhaust ventilation, aeration is used: air exhaust through the transoms of the upper tier and inflow through the transoms of the lower tier. When the outside air temperature is 10 C and above, through ventilation is allowed using lower tier windows for air flow. Aeration and ventilation must be organized in such a way that the possibility of drafts in the workplace is excluded.
Fans of boiler room ventilation systems must be explosion-proof. The requirements for electric motors and starting equipment of these fans depend on their location: motors installed in the boiler room itself must be explosion-proof, and when installed in an adjacent room isolated from the boiler room, they must be of a normal design.
The peculiarities of the ventilation device for boiler rooms, and primarily gasified ones, include the fact that the air flow rate of the blowing units that provide its supply for combustion must be included in the overall air balance of the room. The main room that requires a reliably functioning ventilation device is the boiler room, where the boilers and the units directly servicing them are installed.
When designing heating and ventilation of boiler rooms, the building codes for the design of heating, ventilation and air conditioning and the instructions in this section should be followed.
In calculations when checking the operation of boiler room ventilation systems to maintain air balance, it is necessary to take into account the air flow for fuel combustion.
Ventilation of the combustion chamber combined with the boiler room is equipped similarly to the ventilation of boiler rooms converted to gas. Bakeries operate throughout the year with an even load, usually in three shifts. The volumes of required air exchange, as well as for boiler rooms, are determined for winter, transitional and summer periods. When calculating the heat balance, heat release from the boiler equipment and from the bread baking oven is taken into account.
Direct day-to-day maintenance of boiler units, gas pipelines, gas control units, draft devices and boiler room ventilation is carried out by maintenance personnel. In this case, the administration is obliged to provide Gorgaz employees with free access to gas pipelines and gas consuming installations.
Boiler rooms should provide closed tanks with a steam cushion for collecting drainage from steam pipelines, condensate from steam-water heaters and heaters of the heating and ventilation system of the boiler room. When condensate collection tanks are located in or near the boiler room, all drains should be directed; into these tanks. At the same time, special drainage collection tanks are not provided in the boiler room.
- Purpose of the ventilation system
- Types of ventilation in a boiler room: advantages and disadvantages
- Basic provisions for arranging an air exchange system
- Boiler room equipment with general house ventilation present
- Main stages of installation
The air exchange system plays an important role in creating a healthy microclimate in any building, especially residential premises. Not a single building can do without it, regardless of whether it is residential or not.
Ventilation diagram for a private house with a boiler room.
Purpose of the ventilation system
Ventilation in the boiler room of a private house helps prevent the accumulation of carbon monoxide in the atmosphere and prevents reverse draft. As is known, such phenomena in the air pose a mortal danger, and with a slight increase of 0.2%, a person loses consciousness and subsequently stops breathing.
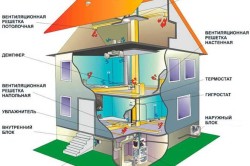
Heating boiler to create optimal conditions work requires oxygen, burning which causes natural combustion. The high power of such equipment is associated with significant consumption of air masses. How can you restore the lost amount of oxygen? To do this, you must follow clear rules:
- Premises equipped with heating equipment require threefold air exchange.
- The height of the building must correspond to 6 m or more. If this condition is not met, the multiplicity of air masses should be multiplied, calculating 25% per 1 m of decrease.
- If it is impossible to ventilate naturally, it becomes necessary to install ventilation equipment.
The air exchange system in the boiler room requires special attention. During operation of furnace equipment, active absorption of oxygen and release of combustion products occurs.
As a result of the lack of high-quality air exchange, the following phenomena are observed:
- an unpleasant aura in the house associated with air pollution, poor health of residents, leading to serious intoxication;
- lack of oxygen leads to poor combustion and reduced efficiency heating equipment.
Return to contents
Types of ventilation in a boiler room: advantages and disadvantages
- Natural.
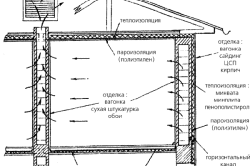
In this option, in a private house, the exchange of air masses with the street is put on stream. The hood is located in the upper part, where the used masses are discharged outside, the supply opening is located at the bottom, due to which oxygen from the outside enters the room. Positive aspects of using natural ventilation:
- installation work is associated with minimal costs;
- the system does not require special care.
Negative points:
- mandatory presence outer wall, impossibility of placing the boiler in the basement;
- the device operates if there is a difference in temperature and pressure inside and outside;
- During the cold period, the room cools down noticeably as a result of the penetration of coolness from the street.
- Artificial.
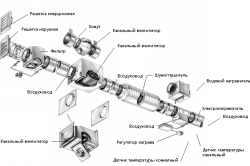
Forced ventilation is used if the air ducts have a long base and there is no natural draft. The supply system is inextricably linked with the air exchange system of the entire building; the exhaust system has one channel for interaction with the street.
Advantages of the forced system:
- the boiler room is located anywhere in the house;
- the effectiveness of the operation of such devices is not determined by external conditions.
Disadvantages:
- significant material costs;
- if the equipment malfunctions, it is simply replaced;
- Usually the burning smell spreads throughout the building.
If it is impossible to install a natural system in a private house, the installed equipment is used in full. You can connect this system to the boiler, then it will start at the moment the fuel equipment is started.
You can reduce material costs by installing artificial device blowing and blowing air.
Return to contents
Basic provisions for arranging an air exchange system

As you know, the ventilation of a private house in a room with a gas boiler can be natural or forced. Its important requirement is compliance with the correct exchange of masses and the absence of danger. To improve the operation of such a device, a number of provisions have been developed:
- Natural ventilation does not allow the use of horizontal sections of air ducts. If this condition cannot be met, an additional fan is required. The horizontal position of such installations does not affect the forced system.
- For natural ventilation to produce results, draft is necessary. To ensure this, the pipe is placed in a vertical position, the height of which is 3 m or more.
An equally important condition for ensuring high-quality ventilation at home will be the location of the heating equipment at the operating point: supply - at the bottom, exhaust - at the top.
From a physics course high school everyone knows that the combustion process is nothing more than a product of an oxidation reaction. To maintain this reaction at a given level, oxygen is required, and the more intense the combustion, the greater the need for oxygen. The method of burning gas or other type of fuel used in boiler plants requires a mandatory influx of atmospheric air to maintain an uninterrupted combustion process. In addition, it is necessary to resolve the issue of smoke removal. These functions are performed by supply and exhaust ventilation.
According to the law, autonomous heat supply points must be equipped natural or forced ventilation system. Unlike industrial construction, in private construction this rule is sometimes not observed. Due to lack of oxygen, with poor supply ventilation boiler room, complete combustion of the fuel does not occur, which leads to a decrease in the efficiency of the boiler and its premature failure. In the absence of proper exhaust ventilation in the boiler room, combustion products enter the room in the form of carbon monoxide and soot, and this poses a threat to human safety.

When the heating boiler is operating, air is sucked from the room to the nozzles to maintain combustion. Previously, there was enough air entering the room naturally through unsealed openings. New ones now building materials allow you to isolate rooms almost hermetically. And if there is no influx of atmospheric air in the room, then the boiler’s performance decreases and a “backdraft” effect may occur, in which smoke will flow into the room. To prevent this, boiler room must be equipped with both supply and exhaust ventilation.
Basically, for normal operation of a small object it is enough natural ventilation of the boiler room. When using a medium-power boiler, it is enough to cut a hole in the wall with a diameter of up to 200 mm, facing the street. A pipe is installed in the hole. From the outside it must be protected from debris, for which it is suitable metal mesh. A check valve is installed on the inside of the pipe, which prevents air from leaking from the room to the outside.
The boiler room exhaust ventilation duct is equipped in the same way. The difference is that on the outside of the pipe it is necessary to install protection from rain or snow (a metal umbrella will do), and a check valve must be installed so that it prevents air from entering the room.
It is advisable to make the supply air duct closer to the floor in close proximity to the boiler. Then the air enters directly into the firebox, without sucking in excess dust and debris, which can impair the operation of the burners. The exhaust air duct must be placed in the ceiling above the boiler. Then the combustion products, rising upward, will immediately be removed outside. This boiler room ventilation system is the simplest and is used mainly in private construction. Its disadvantage is the inability to regulate air exchange. In addition, the air exchange itself depends on climatic factors.
The system does not have these disadvantages artificial ventilation of the boiler room. Typically, such a system is installed when it is impossible to provide the required volume of air naturally, or for large industrial boiler houses. The reason may be that the heat generator is located deep in the room and the air duct will be too long.

Another name for such a system is forced ventilation of the boiler room, because the air moves through the air duct not naturally, but under force. The fan built into the system forces him to do this. Ducted systems typically use ducted fans. When calculating the supply air duct to the boiler room, it is necessary to select a fan based on the maximum air flow, taking into account possible overflow of up to 30%. This value depends on the length of the air duct and the presence of bends in it, etc.
To minimize installation costs for boiler room ventilation, the fan can be installed in only one part of the system. However, to guarantee uninterrupted operation, it is better to mechanize both the supply and exhaust air ducts.
When installing forced ventilation in boiler rooms that operate on liquid fuel or gas, it is necessary to choose explosion-proof fans. The housing of such a fan is made of copper or aluminum to prevent sparking, which could lead to a fire. For ease of control, the system can be automated by coordinating the fan switches with the fuel supply.
The compulsion system is the only difference between artificial ventilation of a boiler room and natural ventilation.
It should also be noted that it is undesirable to connect the boiler room ventilation system with common system air supply, as this can lead to combustion products entering the general system.
If the boiler room does not operate in automatic mode, but requires the presence of personnel, then it is necessary to control the air temperature in the room and, if necessary, preheat the supply air.
You may also be interested in

Block-modular boiler houses provide for the distribution of electricity to electrical receivers of boilers, burners, electric motors of pumps, and electrical receivers auxiliary equipment and management.

Any calculation of the cost of a boiler room begins with a thorough analysis of the data from the questionnaire. Based on background information questionnaire for the boiler room to produce the initial price and selection of technological equipment...

In many ways, the operation of the enterprise depends on the uninterrupted supply of heat and hot water. Modern cities are almost completely gasified - in other words, city utilities provide private owners and companies with a full range of services. But city lines and highways are often in mediocre condition, which leads to constant interruptions, untimely heating or other situations that negatively affect the operation of the enterprise.

Individual boiler houses are gradually conquering the domestic market, previously occupied exclusively centralized heating. According to experts, in the next 10-20 years the number of autonomous low-power boiler houses will increase by approximately 1.5–2 times.

The installation of an industrial boiler room differs little from the assembly and commissioning of a boiler room intended, for example, for heating public utilities, social or administrative buildings. It consists of several main stages.