Steel trusses are widely in demand in most areas of industry; they are indispensable in the construction of residential buildings and warehouses, mechanical engineering, and furniture production.
They can be the basis for absolutely any structure, be it stadiums, bridges, advertising platforms, overpasses and much more, including for a farm made of profile pipe. There are even chimneys with a truss base. For smoke, it is additionally protected from high temperatures.
However, almost all types of such structures have special properties. We will talk about them in more detail now.
Basic information
Metal frames from a profile (a canopy truss is a frame assembled from steel rods, which is used as a ceiling for any space or as a basis for the roof of a building and its body.
It is a “skeleton” for a farm made of a profile pipe, which is subsequently lined with roofing materials and turns into a strong, reliable, but at the same time relatively light canopy or building frame.
All such systems consist of a main zone, which is a load-bearing beam, gratings - the main part of the system, and racks or columns that hold the metal frames above the ground.
About the benefits of use
Metal frames, which are lattice truss structures made of profile pipes, have a number of undeniable advantages in comparison with solid floors:
- Minimum weight;
- Good strength
- Financial savings;
- Long service life;
- Endurance: the frame nodes of the square part are as strong as possible, allowing high loads to be carried very easily;
- Possibility of installation of geometrically complex systems.
There are several characteristics according to which such systems are divided into certain types, the main one being the number of “layers” of the structure; according to this parameter, two groups of metal frames are distinguished:
- The first series includes buildings in which all elements are located in the same plane;
- The second series is supports, which are a hanging system. It includes two belts: lower and upper.
Types of series, their advantages and disadvantages
The type of projected single-slope truss made from a profile pipe will be determined by several factors. A simple example is the maximum load on the system, the span length, the nominal slope of the system and the location where the floor will be placed.
The next separation parameter is the degree of inclination and strength.
A series of samples with a slope angle of 12-22-30 degrees
Their height should be one fifth of their length. The main advantage is the comparative ease of the overall system.
If the span length exceeds 12 - 14 meters, then the braces must be installed in it from top to bottom, and a panel with a length of 150 to 250 centimeters should be mounted on the top one. As a result, the building system, over 14 meters long, consists of two belts with an even number of panels.
In industrial production, standard ones with a profile, having a span of more than 20 meters, are strengthened with a special metal rafter structure, which is supported by support columns.
An interesting representative of this series is Polonso, which consists of two triangular structures connected to each other by a tie. Features allow you to get rid of long braces in the middle panels, which significantly reduces the overall weight of the product.
Triangular with prof. – chief representative this category is the most popular series in household use
A series of samples with a slope angle of 12 - 15-22 degrees
The height of such samples is 1/7 of the span length. If operating conditions require an increase in its height to the limits of 0.16-0.23% of the total length, then the lower chord is made in the form of a broken connection. The maximum length for such frames should not exceed 20 meters. An example can be seen in the picture below.

A series of samples with a slope angle of up to 12 - 15 degrees
If the angle in the project does not exceed 12 - 15 degrees, it is best to use trapezoidal ones. The height of such models is determined by dividing the span into 7, 8, 9 or 12 parts, depending on the specific case and the exact angle of the roof.
In a situation where there is no provision for attaching a suspended ceiling, the reinforcing braces can usually be replaced with a triangular lattice.
The optimal length of the panels is from 1.5 to 2.5 meters. The main advantage of trapezoidal is the high resistance to longitudinal bending, which is achieved due to the presence of short posts.
Now let's look at other features and varieties. First of all, they are divided by shape and outline.
Depending on the form, they are divided into the following categories:
- series arched with profile;
- series with a profile straight line;
- single-pitched with profile;
- gable series with profile.

Division according to the outlines of the metal structure of the main belt:
- With parallel belt. The advantages of this type of metal structures, which are the best option For soft roof, the installation is simplified, since they consist mainly of identical parts, while the sizes of the rods used to create the belt and grille are the same. They also involve few joints.
- Single-pitch. Their main advantage is rigid components with a professional profile, which allow them to withstand significant external loads, and the cost-effectiveness of the metal structure, due to large quantity necessary materials for its construction.
- Polygonal - capable of carrying a lot of weight, but having a complex and labor-intensive metal structure to install and have good strength.
- Triangular - the main type of metal structures for arranging roofs with a large slope. The only drawback of which is the large waste of prof. for the construction.
They are also divided according to the shape of the pipes used in their production. They are distinguished from round and rectangular. Also found in square ones. Example in the picture.
Creating a farm with your own hands from start to finish (video)
The calculation and manufacture of trusses from a profile pipe with your own hands takes place in several stages; let’s look at each of them in more detail:
- At the beginning, the calculation of trusses begins from the need to calculate how long the metal structure you will design. To correctly calculate the drawings, we use an engineering calculator.
- Next, select the main contours of the key belts. The choice is made depending on the slope of the roof and the type of roofing materials used. We put everything on the drawings
- At the third stage, it is necessary to finally determine all the final dimensions of the metal structure: its duration depends on the angle of inclination, and the height is determined by the length, type of ceiling and the limiting weight of the metal structure. Also, if the metal structure is not produced construction site, it is necessary to take into account such factors as transportation to the installation site. An engineering calculator will help in this matter.
- If calculations of the truss have shown that the length will be more than 12 - 36 meters, then it is necessary to calculate the construction lift of the roof. If a triangular pipe is calculated from a square pipe, its angle of inclination should be 12 - 45 degrees.
- Now we calculate the truss and the size of the roof panels to be installed. In this process, it is necessary to consider the load-bearing capacity of the roof, that is, the permissible load that it can support. For this calculation, it is correct to use a calculator.
- The final stage is to calculate the main nodes with rectangular pipes and the distance between them.
This completes the design of rectangular pipes. To accurately calculate the design of trusses, we advise you to adhere to the following recommendations.
In addition, it would be correct to ask a professional designer to tell you how to calculate the truss correctly, check the final result of your work and, if necessary, make the necessary amendments to it. The truss designs with a profile pipe in the project must be reproduced with your own hands in the form of a drawing.
The factor of primary importance is the limit load on the final structure; never forget to take this into account when calculating arch trusses.

When choosing a standard size for a truss made of a profile pipe, it is recommended to give preference to rectangular or square ones, since they have two stiffeners, with which the arched truss guarantees maximum stability and strength even when there are heavy loads.
Choose only high-quality structures made of alloy steel, with a high carbon content - this is a necessary condition for metal resistance to corrosion and negative environmental influences.
In this case, the wall thickness and diameter of the structures must correspond to the load-bearing capacity laid down in the design.
Proper manufacturing of trusses or welding of trusses from a profile pipe with your own hands is impossible without observing the following principles:
- The main elements from which the arched truss is made with your own hands are connected to each other using paired corners and tacks;
- The elements of the lower belt are mated (they need to be welded) using equilateral corners;
- The frame of the truss in the upper chord should be joined by I-angles with sides of different lengths (they are joined together on the shorter side);
- If the structure is very long, overhead plates and pair-type channels are used as connectors for its main parts - which serve as load distributors and which need to be welded together;
- All braces should be mounted at an angle of 12 - 45 degrees, while the racks should be mounted at an angle of 90 degrees.
- After the base is assembled, you need to weld the trusses from the profile. A prerequisite is to control the quality of each weld, since reliability depends on them.
- Tubular steel trusses, when ready, are coated with special anti-corrosion liquids and painted.
This is one of the types of construction products obtained by rolling metal on special machines. Profile pipes are called pipes with a non-circular cross-section. The cross-section can be oval, square or rectangular.
Pipes are made from steel (St3SP, 09G2S), including stainless steel. Initially, their shape is round. The round pipe is then deformed using hot or cold methods. The reliability of the weld is also monitored (this is required by GOST).
Minimum dimensions of profile pipes Russian production. 15x15 millimeters. Maximum dimensions. 450x350 millimeters. Pipe wall. 1.12 mm, length - 6.12 m. These parameters depend on GOST, as well as on the specifications according to which the pipe is produced.
Advantages of a metal pipe truss
- Resistance to deformation even under heavy loads.
- Small mass, since there is a cavity inside.
- Low cost, since little metal is required to manufacture hollow metal elements.
- The ability to build complex structures with a minimum of effort.
- Durability and strength.
Where are profile pipes used?
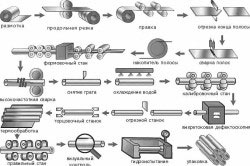
The main areas of their application: construction, agricultural engineering, furniture production. Various metal structures, frames for future buildings, various floors, supports and spans are made from them. Pipes are also used in the construction of advertising posters.
Pavilions for exhibitions, shopping malls, sports facilities, warehouses, industrial structures and buildings, bridges, overpasses, lifts, etc. are built from this material.
The scope of pipes depends on their shape. Flat-oval pipes are flexible, they are used for the manufacture of furniture, as well as decorative elements. Rectangular and square pipes are used to make structures that are placed on a flat surface (building reinforcement, frame spacer structures).
Profile pipes are needed in building structures as supports and fasteners, for example, in construction trusses, which will be discussed below.
Profile pipe truss
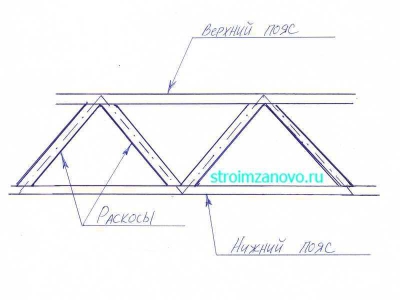
A farm is a system that is the core building structure. It does not change geometrically when its rigid nodes are replaced with hinged ones. If the rods are not misaligned and there is no extra-nodal load, only tension/compression appears in the component parts of the truss. Trusses are created from straight rods that are connected at nodes. Thus, this is a hanging structure consisting of two belts: upper and lower, as well as braces and racks.
The elements that make up the truss: support brace (sprengel), brace, belt and stand.
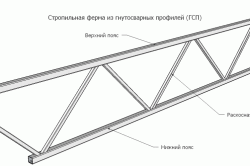
It is difficult to imagine modern construction without trusses. They are used, as a rule, to cover large spans. This is how bridges, factories, sports complexes, pavilions, stages, podiums, etc. are built.
Metal trusses can be purchased ready-made. It is very difficult to independently make the correct calculation of the load on each part of the system, without making a mistake when choosing the material for the structure. Next, you will need to install the system correctly, otherwise a roof truss made from a profile pipe will not serve you for a long time.
Which truss design needs to be chosen will be determined by the location, roof slope angle and required span length.
Below we will talk about the types of roof trusses. All of them can be made from profile pipes.
Roof slope angle 22 – 30 degrees
If the design of the house you are building indicates 22.30 degrees and you want to cover the roof with slate, make an iron or ethernite roofing, it is better to choose a triangular truss, the height of which will be one fifth of the span length. Such a truss weighs little.
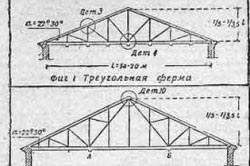
If the span is 14.20 meters long, choose a design with downward braces, since light weight also plays a big role here. Upper part the truss must have a panel 1.5 long. 2.5 meters. Both belts of the structure are made up of an even number of panels. If we take into account the dimensions written above, for such a farm the number of panels should be eight.
If an industrial building is being constructed, the trusses are mounted on metal rafter structures. These structures are connecting elements for supporting columns. The length of the spans in this case. 20.35 meters. Installation of the Polonceau truss is required. This is a structure of 2 triangular trusses, they are connected to each other using a tie. This construction makes it possible to avoid long braces in the panels in the middle, because in order to resist longitudinal bending, they must have a very large cross-section, which will make the entire structure many times heavier. The upper part of the truss is divided into twelve or sixteen panels. The panels are 2.2.75 meters long. If the ceiling is attached to trusses, the tie is attached to the chord nodes at the top.
Roof pitch angle 15 – 22 degrees
As calculations show, in this case, the height of the truss is one-seventh of the span length. Flight. up to 20 meters (if more, it is better to do Polonso). To increase the height of the structure to 0.23 of the span length, the belt located at the bottom is made broken.
Thus, metal trusses weigh about 30 percent less compared to triangular structures. To use these eight-panel trusses, the attic walls must be enlarged.
Roof slope angle 6 – 15 degrees
The roof slope is small - trapezoidal trusses are installed. The truss will weigh the least if its height is equal to one-seventh or one-ninth of the span length.
If hanging from the ceiling structure is not intended, a triangular lattice is needed as braces. The calculation of the number of panels is carried out by analogy with the calculation of panels for a triangular structure. If the length of the attic walls is insufficient, roof fractures are made at the supports. When it is necessary to suspend the ceiling, all panels of the truss must have the same length (in both chords) 1.5-2.5 meters, and racks are added to the braces. To prevent metal structures from being heavy, a lattice is used in which the compression force is absorbed by short posts.
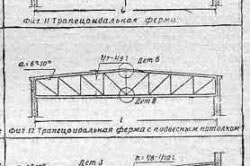
Scheme of a truss for a tilt angle of 6 - 15 degrees.
In the case where a geometrically complex ceiling is expected and its middle part needs to be raised above the truss supports, this is a more suitable option. Polonso farm.
If you need an even greater ceiling height from the supports, you should opt for a polygonal rafter truss. In such designs the lower belt is raised.
Different sizes of the radius of the arch of the structure are possible. It is usually determined by external constraints (where the building will be located, how high it can be, etc.), the size of the canopy, and the client’s requirements. The size of the radius determines the price of the farm and the complexity of its design (the larger, the higher).
However, we must remember that the higher the truss, the greater the load-bearing capacity of the canopy. In winter, there will be little snow on such a roof. The load-bearing capacity of the roof is also related to the number of stiffeners (the more ribs, the stronger the truss). Welding of truss parts must be carried out mechanized. To ensure the safety of a structure, the accuracy of construction is important.
Among the types of trusses there are arched, 2-pitched, 1-pitched and straight.
Sheds such as metal trusses are difficult to construct compared to other types of sheds. But it is a very reliable design if it is installed correctly. In winter, more than one ton of snow ends up on the roof, maybe several tens of tons (this depends on the area of the roof). First of all, farms have the task of retaining this mass. The design distributes the load across the support pillars and joists, successfully coping with the task. So, a construction farm. a very important element of the roof.
Profile pipe. excellent material for making roof trusses. Inexpensive, lightweight, economical and durable.
Select pipe sizes for canopies based on these data:
- 40x20x2 millimeters. small canopies, width up to 4.5 meters;
- 40x40x2 millimeters. canopies, the width of which is up to 5.5 meters;
- For canopies over 5 meters, the following material sizes are possible;
- 40x40x3 millimeters or 60x30x2 millimeters.
Farms should not be further apart than 1.75 meters.
The construction industry is growing rapidly. Until recently, buildings were erected from stone. Nowadays, structures that are built much faster are very popular, thanks to use of the lung, but reliable material. steel.
Metal trusses ensure safety and therefore must comply with certain state standards:
- GOST 23118-99 (on general specifications for steel structures).
- GOST 23119-78 (on requirements for the production of trusses when welding of corners is required).
- GOST 23119-78 (specifications for the production of metal trusses, welding of profile pipes).
Drawings of metal structures are combined into a set of drawings of the KM brand - metal structures. The drawings of this brand include:
General data – title page;
Drawings of views, plans, sections;
Layout diagrams of structural elements;
Drawings of nodes.
General data on metal structures includes various statements and specifications necessary for completing documents and products, as well as installation of metal structures.
Layout diagrams of structural elements are made on a scale of 1:100, 1:200, 1:400. The diagrams show the location of individual structural elements and indicate their brands. If the dimensions of the longitudinal structural elements significantly exceed the dimensions of the transverse elements, then the latter are drawn on a larger scale.
Working drawings of the KM brand must contain complete data for the development of KMD detail drawings, drawing up estimates and ordering metal.
KMD drawings are developed, as a rule, in the design departments of metal structures factories and contain all the necessary data for the manufacture and installation of structures.
Drawings of metal structures are carried out in accordance with the requirements of GOST 2.410-68 ESKD standards " General rules execution of drawings”, as well as the State Standard of the Republic of Belarus “Metal structures. Rules for the execution of drawings of the KM brand." And GOST 21.101-93 “Basic requirements for working drawings.”
One of the features of making drawings of metal building products (structural elements) is the system of arrangement of views:
top view in projection connection above the main view;
bottom view - under the main view;
right view – to the right of the main view;
left view – to the left of the main view.
In this case, each view (except the main one) must be marked in the drawing with a capital letter. The direction of view is indicated by an arrow marked with the corresponding letter (Fig. 5.1).
Rice. 5.1. Location of views on construction drawings
Drawings of metal structures, views and sections show all visible parts of structures and their connections located on the face closest in the direction of view. Of the invisible parts, only those that are located close to the visible ones are shown (Fig. 5.1).
If necessary, on the drawing of the metal structure, its geometric diagram is drawn with solid main lines (Fig. 5.2).
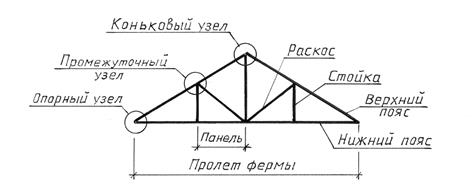
Rice. 5.2. Geometric diagram of a truss
For symmetrical structures, draw a diagram of half of the structure. The dimensions of the distances between the intersection points of the axial lines of the rods are plotted above the diagram lines without extension and dimension lines (Fig. 5.3).
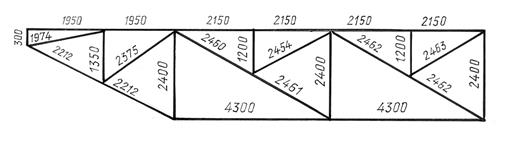
Rice. 5.3. Geometric diagram of half of the structure
In addition to the dimensions, if necessary, the calculated forces with the corresponding signs are applied to the geometric diagram.
If the simultaneous application of dimensions and forces in diagrams of symmetrical structures makes it difficult to read the diagram, then it is drawn out completely, with the dimensions applied on one half of the diagram and the forces on the other (Fig. 5.4).
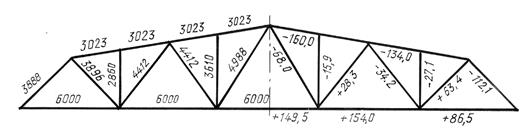
Rice. 5.4. Geometric design diagram
Choosing the outline of the trusses is the first stage of their design. The outline of the trusses depends on the purpose of the arms, the type of roof, the type of connection of the trusses with the columns (hinged or rigid) and other features of the design situation.
The outlines of some types of trusses are shown in Fig. 5.5.
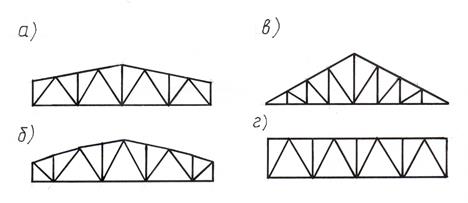
Rice. 5.5. The outlines of the trusses: a) trapezoidal;
b) polygonal; c) triangular; d) with parallel belts
Individual elements of metal structures are connected to each other by welding, rivets or bolts.
Conventional images and designations of seams of welded joints are performed in accordance with GOST 2.312-72. ESKD. This GOST is used when making mechanical engineering drawings, drawings of the KZh brand.
In drawings of building metal structures, conventional images of seams of welded joints are used in accordance with GOST 21.504-2005 “System project documentation for construction. Metal structures. Rules for the execution of drawings of the KM brand", which was introduced in connection with the abolition of SN 460-74 on the territory of the Republic of Belarus (Table 5.1). In accordance with this GOST, seam designations are placed directly above or below the image of the corresponding weld, regardless of whether the seam is visible or invisible (Fig. 5.6).
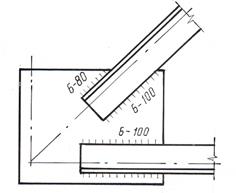 For example, the inscription 6-80 above the image means: the seam has a length of 80 mm with a leg of 6 mm.
For example, the inscription 6-80 above the image means: the seam has a length of 80 mm with a leg of 6 mm.
Metal structures are used in all types of buildings and engineering structures.
Rice. 5.6. Designation and placement
sizes welds
Necessary material of all designs are: rolled steel (angular, I-beam, channel), sheet steel, steel pipes. In Fig. Figure 5.7 shows the most common rolled steel profiles.
Table 5.1.
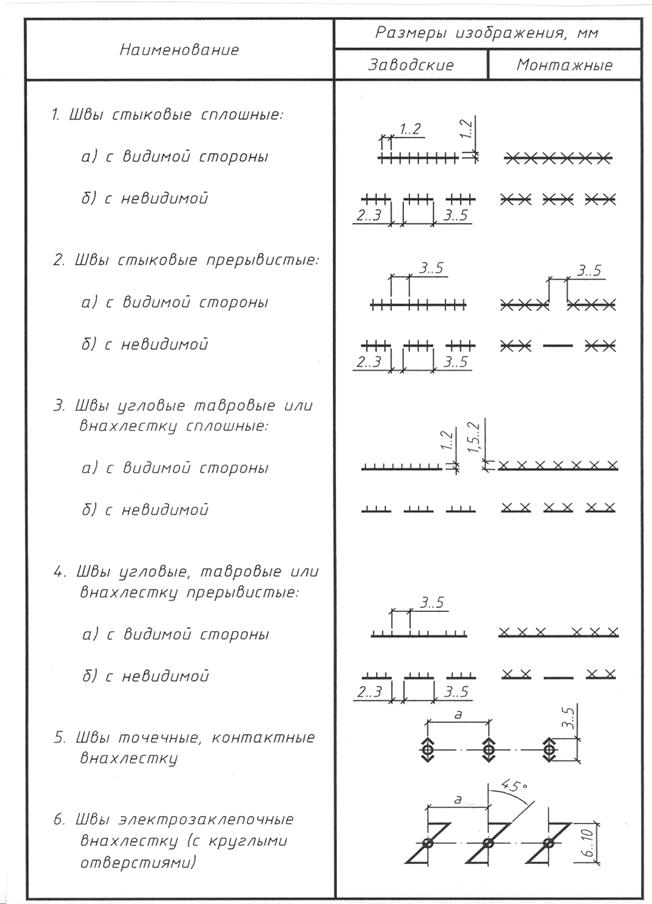
Rice. 5.7. Rolled steel profiles: a) equal-flange angle;
b) unequal corner; c) T-profile; d) I-beam;
e) channel; e) zeta profile
Elements defined by quantities b And h , are called the flange and wall of the profile, respectively. In Fig. 5.8 gives the names of the corner profile elements, Z 0 - the distance from the butt to the center of gravity of the corner.
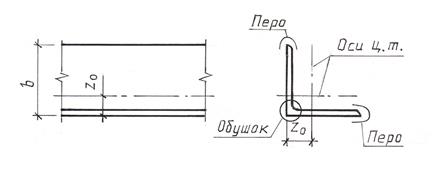
Rice. 5.8 Angle profile elements
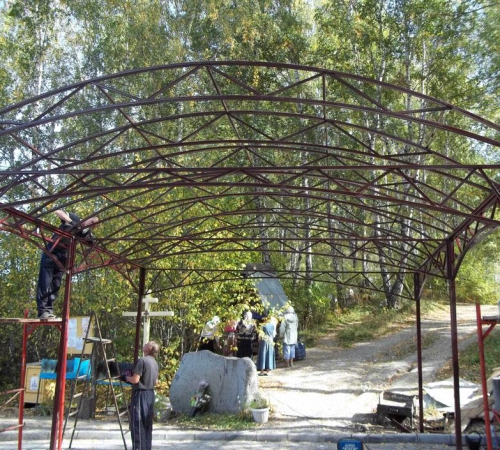
Trusses made from profile pipes in suburban areas are mainly used for the construction of all kinds of sheds. They differ from other structures in strength, durability, light weight, and the ability to construct long-length floors.
Construction trusses can be purchased ready-made and assembled at the installation site, but most often they are made by hand from metal profile. In this case, you can make trusses of any size, any length and number of elements, and the cost of the entire structure will be cheaper than if you buy ready-made ones.
The disadvantage of making trusses from a profile pipe with your own hands is the high duration and labor intensity of the work. A large number of metal elements will need to be removed from rust, cut, welded and painted.
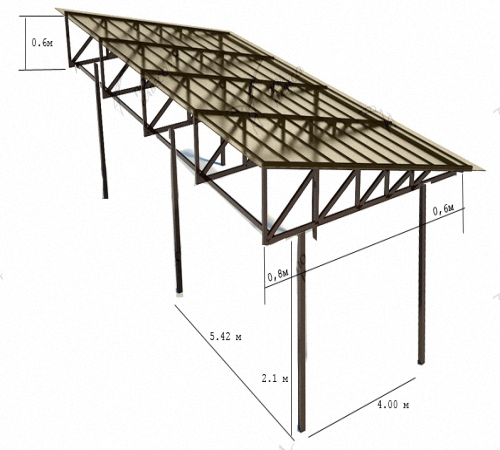
On our country plot, we also decided to make a canopy from. We will use metal ones as supports; to strengthen the structure, we will manufacture and weld trusses from a profile pipe to them.
First of all, let's calculate the quantity and size of the profile pipe required for the manufacture of canopy supports and the trusses themselves. For the racks we will need a profile measuring 60 by 60 mm, for the upper chord of the truss - a 40 by 40 mm pipe, for braces and the lower chord - 20 by 40 mm. It is better to use a pipe wall thickness of at least 3 mm. Thick metal is easier to weld, thinner walls often burn through, and welding them requires some skill.

So, some of the metal was bought at the base, the other part was left over from.Use a garden drill to drill a hole in the ground to a depth of 1 m, install a pipe of the required length measuring 60 by 60 mm in it, level it and fill it cement mortar, mixed with crushed stone. 
In the same way we will install three more pillars. A total of 4 supports were concreted on one side. To set them at the same height, we used .

Let's step back 2.5 m from the first line of pillars and install 4 more supports, only 50 cm taller than the previous ones. We will have a lean-to canopy, so we made the first posts higher than the second ones. These supports will support the canopy roof. In order for the roof and racks to withstand the mass of snow that will accumulate on it in winter, they need to be strengthened. The most common option for these purposes is to make trusses and weld them between the posts.

Let's move on to making the farm. A parallel quadrangular building truss looks like this.
Let's start with the top belt. Let's take a 40 by 40 pipe, cut it to a length equal to the distance between the first pillar and the last, and electric weld it to the top of each support. The top belt is ready.

Next, we use a 40 by 20 profile pipe, measure the distance between adjacent posts and cut it with a grinder. Let's step back 20 cm from the top chord and at this level weld a piece of pipe to the supports, placing it flat. If there is no assistant, one end of the pipe can be secured by placing a support under it, and the other can be held with a hand free from the welding machine holder. We will check the horizontal level of the lower belt using a building level.

We will also weld two more profile pipes between the supports.

Now you need to weld braces between the upper and lower chords of the truss. It is through them that the strength of the structure is achieved. If the rafters are simply placed on the top chord, without a truss, then the weight of the snow will deform the pipe and the canopy will collapse.
The braces are welded between the chords at an angle of 45 degrees. First, take a protractor and determine the angle of inclination by making a mark on the pipe. Then we will lean a piece of pipe 20 by 40 against this place and draw a pencil on it in the place of the intended cut. Use a grinder to cut off the excess metal.

Using this template we will make the required number of segments.

All we have to do is weld them to the belts of the truss. First, the braces are attached to the pipes at small points so that they stay on the structure.

It is better to start welding them on both sides alternately. When all the pipes have been grabbed, they can then be scalded on all sides. This is done so that the truss does not move and does not change its geometric properties. It is especially important to follow this sequence if you are welding the truss on the ground and its chords are not rigidly secured between the supports.

Adjacent braces are located at a short distance from each other. Conventional lines are drawn along their middle; these lines should intersect at the highest point of the upper belt and the lowest point of the lower one.
We will weld the braces between all the supports of the future canopy. This work is painstaking and time-consuming. But you need to learn how to weld metal yourself: firstly, this skill will always be useful in housekeeping, and secondly, you will save a large amount of money, because professional welders charge for each seam. Imagine how many welds need to be made when making a construction truss and how much it will cost.

![]()
The first canopy truss is ready. Let's start making the second farm in the same way. Here, too, we will first weld the upper belt.

On the advice of experienced welders, it is more convenient to use a clamp instead of stops to support one side of the pipe. It is better to buy a welding mask with automatic darkening, especially for beginners.

As a result, after much work, we ended up with 2 building trusses for a canopy.



We will install on wooden rafters, laying them on posts with trusses. To attach the boards to the top chord we use metal corners. Take a piece of corner with a wall thickness of 4 mm and use a grinder to cut it into several short pieces.

Using a drill, we will drill two in them.

We weld the corners to the upper chords of the trusses 60 cm apart. Subsequently, having installed the rafters, we will screw them with two self-tapping screws to each corner.


The supports with trusses for the canopy are ready, all that remains is to paint them with paint for metal surfaces.

When the paint has dried, we will begin installing the polycarbonate sheathing.


VIDEO
If necessary, profile pipes are used in the construction of a canopy. Trusses made from profile pipes are a durable, strong and economical design that allows you to cover any span. We will consider further how to build trusses from a profile pipe.
Features of the design of a truss made of profile pipes
Trusses from a profile pipe are constructed from a metal profile, which is made by rolling and processing the metal using special machines; depending on the type of section, profile pipes are divided into:
- oval profile,
- rectangular section,
- square section.

High-quality steel is used for the production of profile pipes. The initial shape of the profile pipe is round. But, after undergoing hot or cold processing, the pipe is deformed into the desired shape. Profile pipes come in different sizes, the minimum section is 15x15 mm, and the maximum is 45x5 cm. The pipe wall thickness is 1.12 mm, and the length is 612 cm.
The size of the span in which the truss is installed affects the load and the cost-effectiveness of material consumption.
Flat type trusses require fastening, while spatial type trusses act as a rigid structure that can withstand any load.
Main components of the farm:
- belts - act as a contour,
- racks,
- braces,
- support brace.
To manufacture a truss, it is necessary to have connectors, which are paired material, gussets, rivets and welding.
Truss made from profile pipes photo
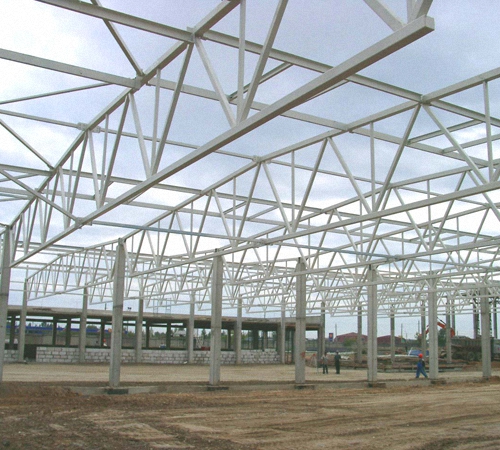

Advantages of using a truss made from a profile pipe
- high strength ensures long service life;
- the use of a profile allows you to build the most complex structures with a minimum of costs;
- affordable price;
- the weight of the truss structure is small, since the pipes inside are empty;
- a profile pipe truss is resistant to deformation, mechanical shock or other damage;
- anti-corrosion - this design is resistant to moisture, and metal pipes do not rust over time;
- the possibility of further finishing using polymer paints, which will give the farm a beautiful appearance.
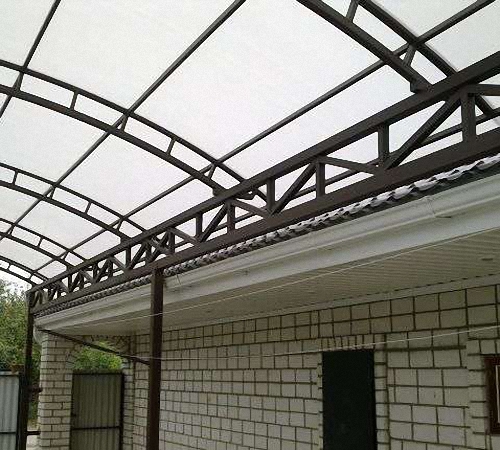

Scope of use of profile pipe trusses
Trusses made from profile pipes are used to construct metal frames, which in the future will become sheds or buildings.
A truss made from a profile pipe works well as a carport in the absence of a garage.
To protect open areas from the sun, trusses are also constructed from profile pipes.
Trusses are used to build bridges or cover an industrial or private building.
Additional trusses made from profile pipes are used:
- at communication facilities,
- power lines,
- transport roads,
- in the construction of bridges, factories, sports complexes or stages.
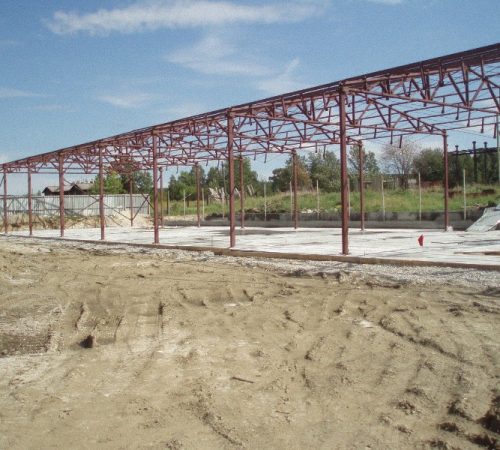

Types of profile pipe trusses
Trusses made from profile pipes are divided into two types. One type of truss is a structure in which all elements are connected in one plane.
Another type involves a truss with the production of a hanging structure, which includes an upper and lower chord.
The choice of design depends on the following factors:
Depending on the slope angle, the following trusses are distinguished:
1. Truss with a slope angle from 22° to 30°. If you have data on the roof slope angle, when constructing a small slate floor, the best option would be to use triangular trusses from a profile pipe. To calculate the height of the truss, the span length should be divided by five. The advantage of this design is its light weight. If the span is large and exceeds fourteen meters, you should choose a design in which the braces are located from top to bottom. A panel is made on the top of the truss, the length of which is from 150 to 250 cm. This design consists of two belts with an even number of panels. When manufacturing industrial trusses from a profile pipe, the length of which is more than twenty meters, they are mounted using a rafter metal structure. Such structures are connected by supporting columns. The Polonso truss is a structure that consists of two triangular trusses connected by a tie. Such a truss prevents the presence of long braces in the middle of the structure, and lightens the overall weight of the structure. At the top of such trusses there is a large number of panels, the length of which is more than 2.5 m. When fixing the ceiling to the truss, the tie-rods are fixed in the upper node of the belt.
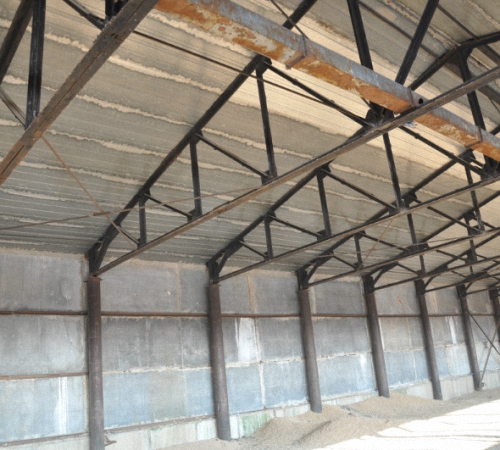

2. In the case of a roof slope at an angle of 15 to 22°, the height of the truss is calculated by dividing the span length by seven. The length of such a truss does not exceed twenty meters; for longer lengths it is better to use a Polonceau truss. To increase the height of the structure, the lower belt should be made broken.
3. With a minimum roof slope that does not exceed 15 degrees, trusses are installed in the form of a trapezoid. The height of such a truss is calculated by dividing the span length by a number from seven to nine, depending on the exact value of the slope. If the truss is not installed directly on the ceiling, then a triangular lattice is used as braces.
According to the shape, profile pipe trusses are divided into:
- single-pitched trusses made of profile pipes,
- gable trusses made of profile pipes,
- straight trusses from profile pipes,
- arched trusses made of profile pipes.
Depending on the outline of the belt, trusses are divided into:
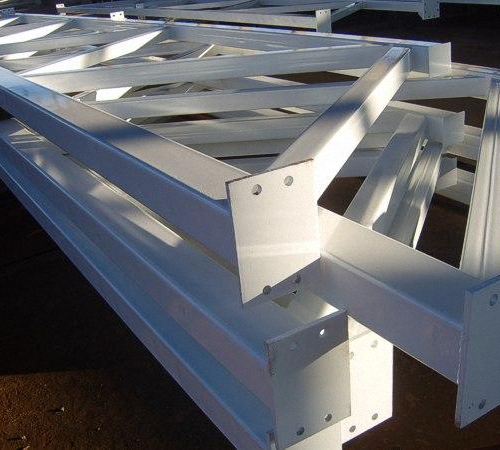
1. Farms with a parallel belt device have the following advantages:
- ease of installation due to the large number of identical parts,
- the length of the rods used to construct the grid and belt are the same,
- availability minimum quantity joints,
- complete unification of the design,
- use with a soft roof.

2. Single-pitch trusses made from profile pipes have the following advantages:
- arrangement of rigid nodes,
- absence of long rods in the middle of the truss,
- complexity, but at the same time economical design.
3. Porigonal type trusses are distinguished by the following features:
- used for constructing buildings that are heavy,
- provide economical use of the profile,
- The construction of a polygonal farm is quite complex and labor-intensive.
4. Triangular trusses are easy to manufacture and are used for steeply sloping roofs. Flaws:
- complexity in the design of support units,
- high profile consumption.
Depending on the arrangement, the gratings in the trusses are divided into
- triangular lattices, most often used in trusses with parallel poles, sometimes in trapezoidal or triangular trusses,
- diagonal type gratings are characterized by labor-intensive execution and high material consumption,
- Individual gratings are made based on the size and characteristics of the farm.
Profile pipe trusses: design calculation
1. Before carrying out calculations for the manufacture of trusses from a profile pipe, you should decide on a diagram that indicates the dependence of the length of the truss on the angle of inclination of the roof.
2. When choosing a scheme, you should decide on the contours of the truss chords. This detail depends on the functions of the structure, the type of roofing materials and the angle of inclination.
3. The next step involves choosing the size of the farm. When calculating the length of the truss, the angle of inclination should be taken into account, and the height depends on the type of floor, possible transportation of the truss and total weight designs.
4. If the length of the truss exceeds 36 m, it is necessary to calculate the construction lift.
5. Determine the dimensions of the panels. The calculation should be carried out based on the load that the farm must withstand. When designing a triangular truss, the angle of inclination is forty-five degrees.
6. The final stage is determining the interstitial distance.
- to calculate a truss from a profile pipe, use the services of a specialist or special computer programs;
- check the accuracy of the calculations several times;
- for the calculation and manufacture of a truss from a profile pipe, a drawing is an obligatory and necessary component;
- be sure to take into account the maximum load on the truss structure.

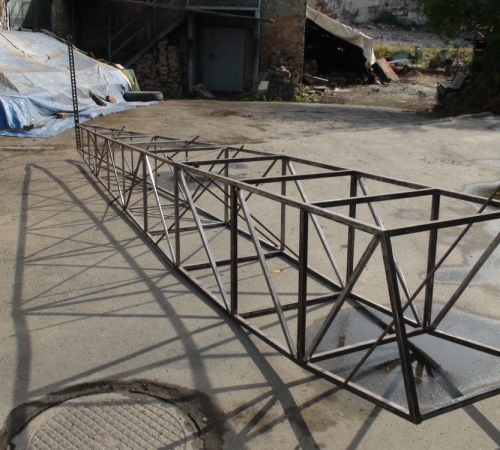
Making a truss from a profile pipe
To assemble or fasten elements, you should use tacks or paired corners.
When constructing the top chord, use two T-angles with different side lengths. Butt the corners together with their smaller sides.
To connect the bottom belt, use corners with straight sides.
When making a large and long truss, overhead plates act as connectors. For uniform distribution loads are applied using pair-type channels.
Install the braces at an angle of forty-five degrees, and the racks at a right angle. To make such a structure, use T-shaped or cross-shaped corners with straight sides, fastened with plates.
Brands are used for the manufacture of complete welded systems.
After completing the assembly of the structure using tacks, begin welding work. Welding is done manually or automatically. After welding, each seam should be cleaned.
The final stage includes treating the system with special anti-corrosion solutions and paint.

1. To lighten the structure of the truss, with a minimal roof slope, use additional gratings.
2. To reduce the weight of the truss structure, with a roof slope of 15 to 22 degrees, arrange the lower chord as a broken one.
3. When installing a long truss, install only an even number of panels.
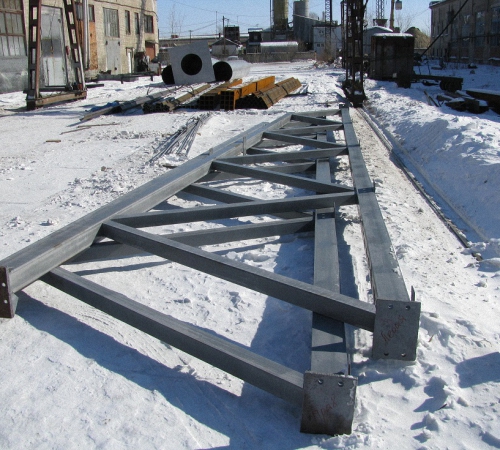

4. If the length of the truss exceeds 20 meters, use the Polonceau truss device.
5. The size and cross-section of the profile for the truss depends on the width and slope of the canopy.
6. The distance between two trusses should not exceed 175 cm.