Discharge of human waste can cause irreparable harm to the environment. To prevent this from happening, special treatment facilities are installed. They contribute to the fact that waste water ah contains fewer pathogenic harmful organisms.
Classification
Water effluents are divided into several classifications according to their type:
- Stormwater treatment. They are also called superficial. Either rain or atmospheric. During precipitation, they form on the surfaces of working structures.
- Production facilities. Wastewater that is generated during technological processes. Large quantity industrial waters complicates this issue.
- Household waters flow from plumbing and residential buildings into the sewer system.
Wastewater contains various types pollution, both organic and mechanical. Their composition and condition may also be different. For example, colloidal, undissolved or dissolved.
Effluents are divided into groups and according to the degree of pollution:
- Domestic water is the most dangerous.
- There are wastewaters that are close in characteristics to atmospheric ones.
- Atmospheric ones are the least polluted.
There are several important indicators when it comes to the degree of purification.
This applies to MACs, or maximum permissible values for various pollutants. And also BOD is the total oxygen requirement, biological.
The following considerations can be used to select the optimal cleaning system:
- The service life of the treatment device should be approximately the same as that of the building served by the system.
- The composition of purified water must meet the requirements established by law.
- The main thing is that the structure can cope with current loads, even with irregular waste receipt, taking into account the changing seasons.
- Open and constant access to all parts is required treatment plant, parts and components.
- It is important to operate as simply as possible, without serious requirements.
- Reliability of equipment in operation.
Depending on the amount of water consumed at the facility, the productivity of the installation is selected. And the amount of water consumed depends on many factors, including the number of people living in the house.
How do wastewater treatment systems work?
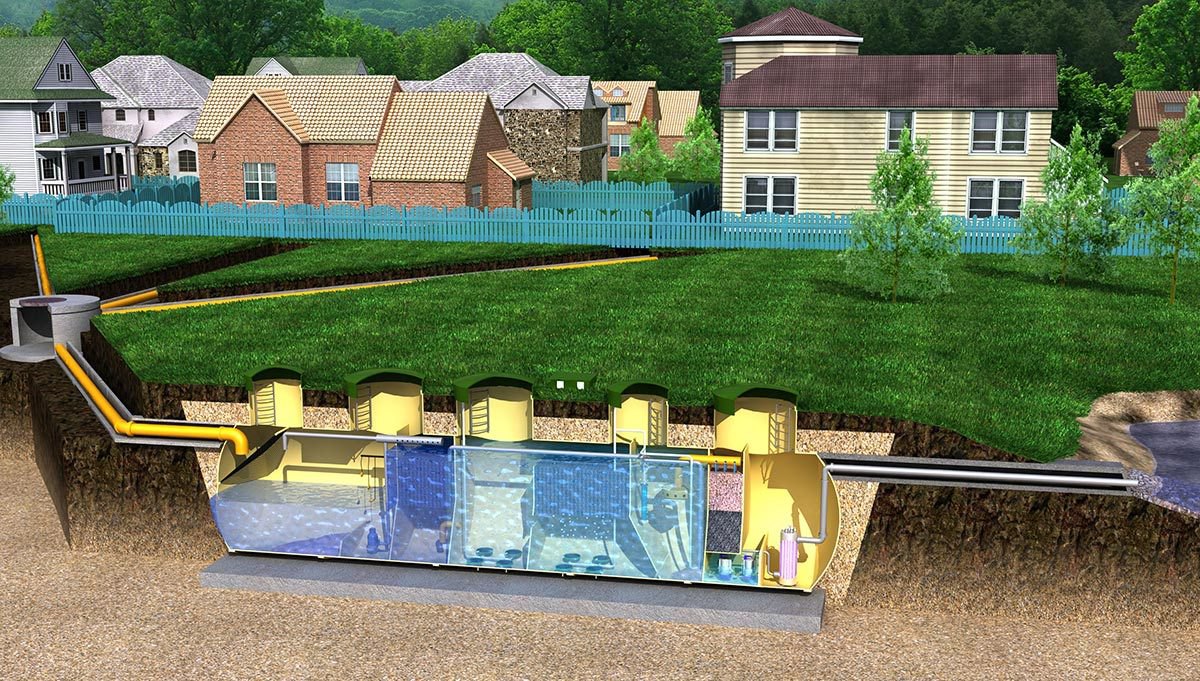
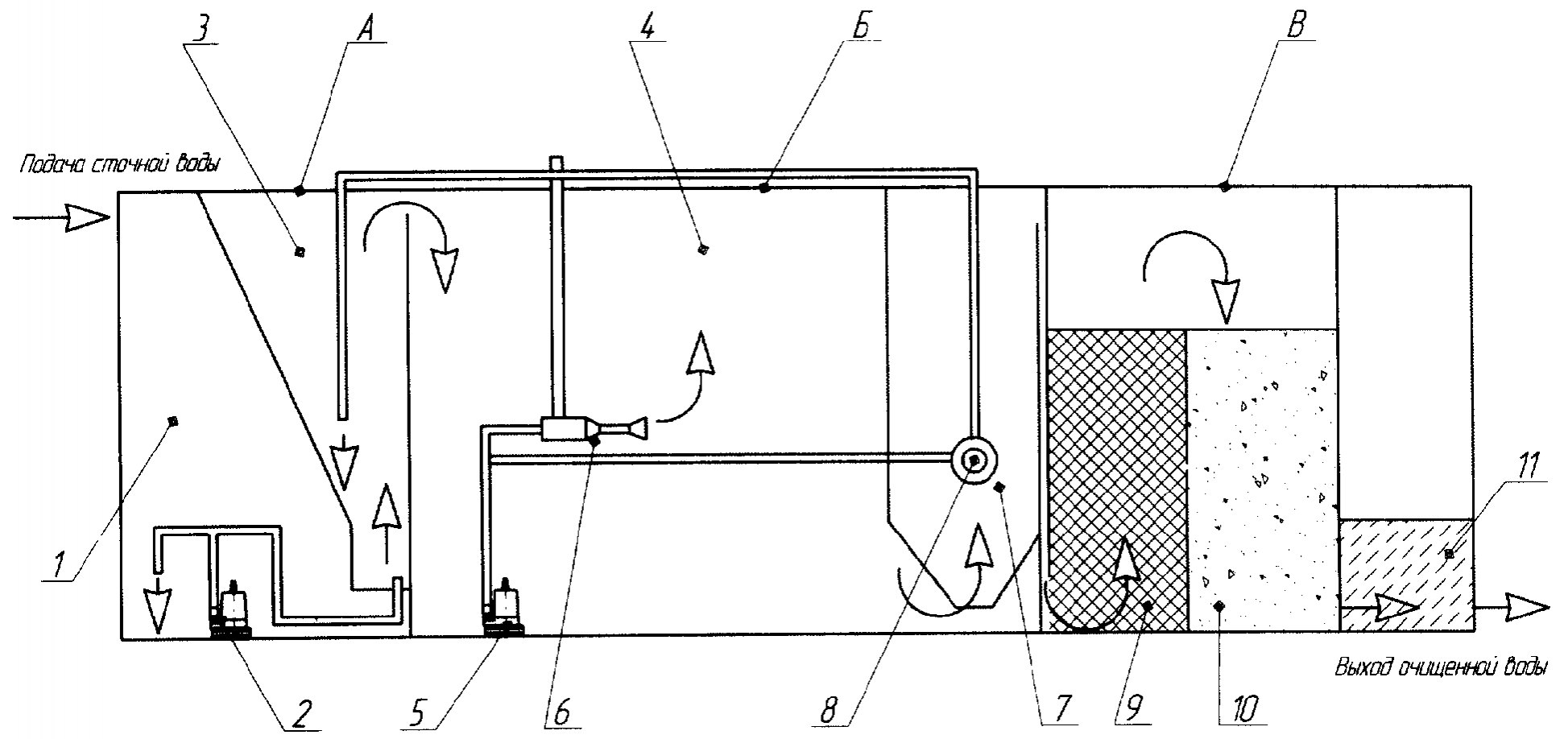
There is a special device called a septic tank - it carries out primary wastewater treatment. Anaerobic bacteria are responsible for the initial decomposition of the liquid. They do not require access to air to operate.
But air must enter the septic tank itself, otherwise it will not be possible to create optimal conditions for the operation of the entire device. It is necessary to combine the action of anaerobic and aerobic bacteria to get the best result.
Air is supplied inside using compressors to ensure greater efficiency during operation. For biological treatment Several types of treatment facilities are used:
- Drainage fields.
- Biofilters.
- Aero tanks.

Water purification in the cottage.
The aeration tank contains aerobic bacteria, which carry out the cleaning. The compressor supplies air inside the device. Liquid is constantly pumped from one container to another. The degree of purification reaches 98 percent.
In a biofilter, wastewater passes through a special layer. The main materials for its manufacture are polyurethane foam, pozolan, and polystyrene foam.
Colonies of microorganisms grow on the surface of such filters. They decompose organic matter into several components:
- insoluble;
- soluble with water.
Wastewater enters the biofilters only in small doses. If the pressure is too intense, the layer will not have access to air in the required volume. This will cause bacteria to die. Thanks to this method, liquids are purified by 90-95 percent. Biofilters are changed from time to time and completely cleaned.
Drainage fields and wells
This is the next stage that is organized during wastewater treatment.
What are drainage fields? This is a system of channels located underground. They are laid out with several layers of materials of natural origin, capable of filtering everything that gets into them. Drainage pipes are laid precisely in these layers.
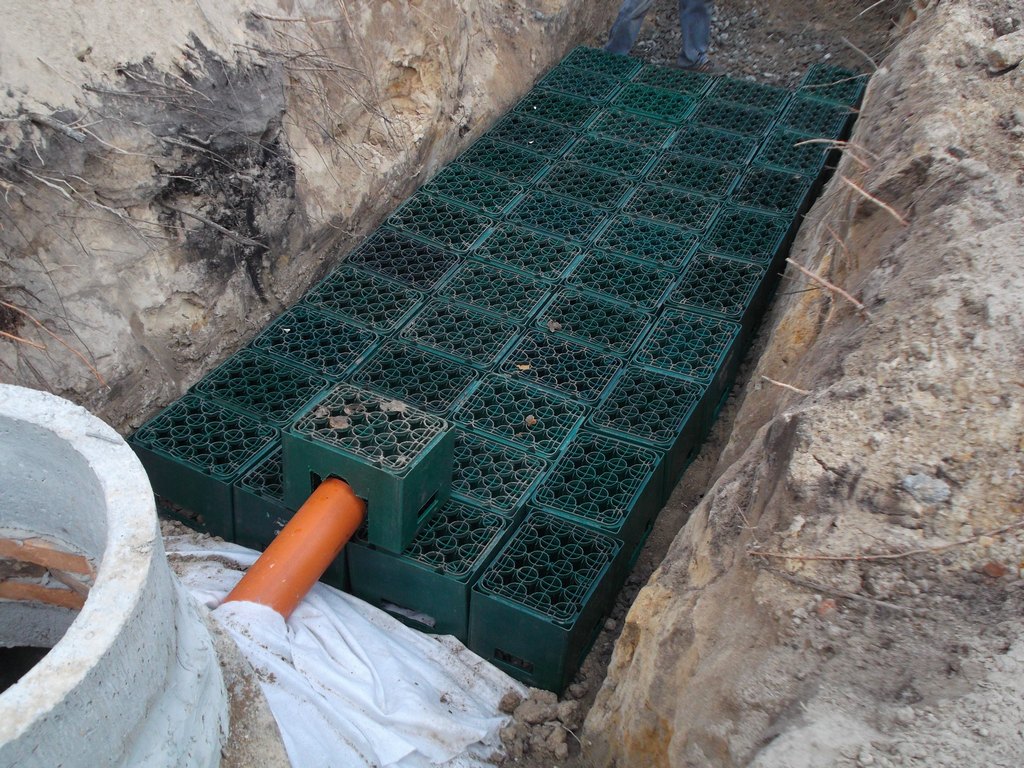

The drainage field is arranged on hills if there are uneven areas on the site. Thanks to this, wastewater flows freely without threatening the surrounding area. 1.5 meters is the minimum required distance between the level where groundwater is located and the filtration field.
Filter wells also carry out additional treatment. Their installation is carried out in several stages:
- We start with the pit. Its diameter should be 0.8 meters larger than that of the well itself.
- We are preparing a concrete screed around the perimeter. The main thing is to leave the center free from concreting. Then water will flow freely through this area.
- We immerse three rings of reinforced concrete into the dug shaft using a regular construction crane.
- We make holes with a 50 mm diameter in the lower ring using a hammer drill. The distance between them should be at least 100 millimeters.
- We fill the bottom of the well, one meter high, with filter material. It can be gravel or broken brick, or any other types of materials. The same backfill is laid between the walls of the well and the rings.
- An inlet pipe is installed in the side hole. The distance from the backfill level is half a thousand millimeters.
- The well hatch must have two holes. One of them is under the exhaust riser, and the other is under the cover.
Design
Competent design is necessary even for treatment systems that are built on the territory of private houses. It is necessary to calculate the arrangement of the site according to environmental and sanitary safety, SNiPam.
Enterprises differ from private houses in the level of complexity of such structures. In addition, in such situations, a regeneration cycle can be used. This means that clarified water is reused. Several factors must be taken into account when designing:
- How much will residential construction cost?
- How safe and environmentally friendly are the technologies?
- What characteristics should be obtained at the output?
- Can the water in the system be reused?
- What volume of wastewater is planned to be consumed?
The market produces household equipment that fully complies with the standards of environmental authorities in the country. The largest circuits have many elements. These are water disposal projects for urban and municipal services, housing and communal services.
Household modular installations- these are devices with a daily productivity of 10,000 - 10 cubic meters. Five hundred thousand is a performance parameter for industrial units. Stormwater also needs treatment, not just industrial and domestic water.
Re-equipment and repair of treatment facilities is a service no less in demand. Engineers solve several problems by drawing up specific projects.

Industrial water treatment.
More details:
- It is necessary to minimize the amount of precipitation.
- Reduce the number of technical personnel, automate the production process.
- Replacement of equipment and technical processes to increase output quality.
- Application of new technologies to improve productivity. At the same time, they try not to increase the volume of structures.
Performers supporting corporate interests in mandatory must participate in project development. Russian legislation speaks about this. More details:
- Adjusters. They will identify errors in execution, conduct demonstration launches, and conduct several tests.
- Facilities suppliers. They can re-negotiate equipment to make more profit.
- Builders responsible for implementation.
- Designers. They will help you pass the examination with minimum requirements and will monitor compliance with industry standards and SNiP norms.
Because of this, tariffs associated with compensation of costs for the operating company increase. You can minimize costs by choosing comprehensive services.
Biological treatment plants BIOX-sgp
Grease traps under the sink Post-treatment units Two-section pump station with sludge storage tank
Wastewater contains a complex mixture of solids and dissolved substances, which are present in very low concentrations. When wastewater enters the treatment facilities of the BIOX model range, deep biological treatment of wastewater occurs. The concentration of organic substances is reduced to an acceptable level or chemically transformed into safe compounds. Technological diagram Treatment of domestic wastewater depends on the degree of contamination and quantity of wastewater treated, as well as economic and environmental considerations.
Biological wastewater treatment is the result of the functioning of the activated sludge - wastewater system, characterized by the presence of a complex multi-level structure. Biological oxidation is the basis of this process and is a consequence of a large complex of interconnected processes of varying complexity: from elemental acts of electron exchange to complex interactions of the biocenosis with the external environment.
Purification of household wastewater using BIOX installations
The nature and concentration of pollutants in wastewater depend on their source. When considering household wastewater, we can conclude that it is contaminated mainly by street garbage, detergents and feces.
Domestic wastewater typically contains more than 99% water, about 300 ppm (mg/l) suspended solids, as well as about 500 mg/l of volatile substances. Deep biological wastewater treatment at our BIOX-SGP installations will purify up to 96% of all contaminants, which complies with the rules and regulations established by Rospotrebnadzor.
If biological wastewater treatment is used to treat domestic wastewater, then this system must include the following components:
- developed by the company "SPETSGIDROPROEKT group" - a 2-section pumping station with a sludge reservoir;
- averager;
- gratings;
- sand traps;
- biological treatment unit;
- post-treatment unit;
- ultraviolet disinfection unit.
Considering the origin of domestic wastewater, it is not surprising that it contains various types of soil and intestinal microorganisms, including aerobic organisms, obligate and facultative anaerobes, bacteria, yeasts, molds and fungi. Therefore, biological wastewater treatment must necessarily include ultraviolet and ultrasonic water disinfection at the final stage of treatment.
Domestic wastewater treatment is affected by temperature fluctuations: temperature drop environment below a certain level, it slows down the activity of beneficial bacteria. In order for biological wastewater treatment to work as efficiently as possible, treatment facilities are used in the form of container blocks connected into a single treatment system, which allows the composition of the wastewater to be brought up to the standards for discharge into fishery reservoirs.
For comfort in a private or country house simply necessary domestic waste, especially if the house already has a water supply. These drains consist of kitchen waste water, bathroom waste water, as well as drains eau de toilette. This drainage system forms a sewer system.
The city sewerage system has a long-term drainage of wastewater and ends at a number of treatment facilities. Such facilities not only clean, but also disinfect wastewater. But if private house is located far from the central sewerage system, then in this case domestic wastewater treatment and their subsequent disinfection becomes the task of its owners.
This problem is solved by creating a local or individual sewerage system, which involves the presence of treatment facilities.
Over the long years of human existence, there has always been a question: where to direct How to clean household waste and prevent environmental pollution. Since then waste water treatment system has undergone virtually no changes. The filtration system is carried out mechanically: grates, meshes and filters purify wastewater from suspended contaminants. In septic tanks, a lot of work is done by microorganisms, for which wastewater is the most favorable habitat. They absorb most of all organic contaminants without leaving behind any contaminants.
When decomposed, organic waste releases a number of gases, high concentrations of which are explosive. Therefore, all treatment plants must be equipped with an active ventilation system.
Household wastewater treatment methods and filtration are of great importance for the environment. Improper drainage can disrupt the groundwater system, which will lead to undesirable consequences.
Currently, the artificial method of biological treatment is widely used; contaminated water is drained into a special settling tank, in which a favorable environment for the habitat of putrefactive microorganisms is artificially created. In this case, the tank is continuously purged with air. This is followed by the second stage of purification and secondary settling tanks. After which the wastewater is sent to aeration tanks for complete destruction of the wastewater using so-called fine-bubble aeration.
MOSCOW STATE UNIVERSITY OF ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING
Department of “Fundamentals of Environmental Engineering and Chemical Technology”
Abstract on water treatment
"Domestic wastewater treatment"
student: Kuznetsova I.V.
Group: N-40
teacher: Bulatov M.A.
Moscow, 2003
|
I.Introduction………………………………………………………………………... | |
|
Sources of formation, quantity and composition of chemical waste products…………...... | |
|
Requirements for the quality of purified water and conditions for their discharge into the reservoir... | |
|
II. The essence of the processes used in cleaning HBSW……………… | |
|
Comparison existing methods cleaning…………………………… | |
|
Physico-chemical methods……………………………………………………………… | |
|
Technological diagram of two-stage wastewater treatment……... | |
|
Sand filter……………………………………………………………… | |
|
Calculation of sand filter……………………...…………………………... | |
|
III.Conclusion………………………………………...………………………… | |
|
IV.References......................................................................................... | |
Introduction Sources of formation, quantity and composition of domestic wastewater
Wastewater from populated areas is formed as a result of human activity - household wastewater (fecal waste, food residues, detergents, soil particles, household waste, etc.) and in the industrial sector - industrial wastewater (process waste, raw material residues, etc. .p.). [ 1]
Domestic wastewater in each locality is the same, namely: wastewater from the toilet (containing fecal matter, paper, detergents), baths, washing clothes (containing a large amount of synthetic surfactants), cooking, washing dishes, cleaning the premises etc. A study of the type and amount of wastewater for each type of named expense item showed that on average, kitchen needs (cooking, washing dishes) account for 15-20% of wastewater from a family, bath and shower 20-25%, toilet flushing - up to 35 %, washing clothes - up to 20%. Toilet and kitchen drains account for up to 75% of household wastewater pollution.
Pollutants in wastewater are in the form of suspensions, colloids and solutions. Up to 40% of pollution consists of mineral substances: soil particles, dust, mineral salts such as phosphates, ammonium nitrogen, chlorides, sulfates, etc.
Organic pollution is very diverse and is formed due to the influx of human and animal waste, and the influx of food residues and raw materials into the water. Organic contaminants include fats, proteins, carbohydrates, fiber, alcohols, organic acids, etc.
The content of organic pollutants in wastewater is determined by indirect indicators: COD (chemical oxygen demand) and BOD (biological oxygen demand). COD expresses the amount of oxygen required to completely chemically oxidize organic pollutants found in wastewater. BOD expresses the amount of oxygen required for the biological oxidation of organic matter by bacteria under aerobic conditions (without oxygen consumption for nitrification). Biological oxygen consumption for domestic wastewater ends after approximately 20 days (BOD total), and the value of 5-day consumption for household wastewater (BOD 5) is, as a rule, 65-70% of BOD total, which in practice allows for a significant reduction time for determining this indicator, and with a sufficient degree of accuracy determine the amount of organic contaminants.
The amount of contaminants in household wastewater per person is determined mainly by physiological indicators and is approximately (in grams per person per day):
BOD full 75
Suspended solids 65
Ammonium nitrogen 8
Phosphates 3.3 (of which 1.6 g is due to detergents)
Chlorides 9
Thus, the concentration of pollution depends only on the amount of water disposal, which corresponds to the degree of improvement of housing.
A special type of pollution in household wastewater is bacterial. Wastewater contains a large number of bacteria, including pathogenic ones, and viruses. Pathogenic bacteria are adapted to exist in the body of humans, animals, and birds. Getting into wastewater (or directly into a reservoir), some of these bacteria die due to the lack of a specific substrate or optimal temperature. Some bacteria retain their pathogenic activity in wastewater or reservoir water. Wastewater may contain tuberculosis bacteria and leptospira. Brucella, tularemia bacteria, Vibrio cholera, etc. All this bacteria persists in water for different periods time. Therefore, Escherichia coli was chosen as an indicator of fecal water pollution. The concentration of cells of coliform bacteria in water determines the degree of contamination of water by bacteria and its suitability for use as drinking water or for cultural and domestic purposes. [ 1]
Domestic wastewater (HWW) is characterized by an increase in the content of mineral impurities, caused by an increase in Na salts and the appearance of phosphates, nitrates, etc. in the effluent. (Table 1)
Table 1.
|
Suspended solids |
0.3-0.5 g/dm 3 |
|
400-800 mg O 2 /dm 3 |
|
|
60 mg O 2 /dm 3 |
|
|
Rigidity |
12.5-25.0 mmol/dm 3 |
|
Total salt content |
1.5-6.0 g/dm 3 |
|
25.100 g/dm 3 |
|
|
15-30 g/dm 3 |
|
|
1.5-3.0 g/dm 3 |
|
|
According to oleic acid | |
|
Polymitin company | |
|
Steorinova's office | |
|
Steonate Na | |
|
Fat people | |
|
Carbamide | |
|
Gipurova | |
|
Amino acids | |
|
Lemon | |
|
Related fats | |
Wastewater treatment is the removal of foreign impurities from it before discharge into a body of water or soil. Wastewater can be divided into several categories:
- household – sewerage;
- industrial - the result of the work of factories and factories;
- atmospheric - melt and rain water.
Not only wastewater discharged by enterprises must be treated, but also household wastewater from sewer systems. Poorly treated water from even a small private home can cause serious damage to the environment.
Previously, sewage was collected in ordinary, so-called cesspools, but due to inconsistency sanitary standards they have to be abandoned. Today, autonomous treatment facilities are used to collect and treat household wastewater, where it is purified by 90 - 99%. After which they can be dumped into open water bodies or soil.
Cleaning methods
Domestic wastewater may contain soluble or insoluble impurities. Depending on the size of the particles contained, they can be divided into:
- emulsions and suspensions – 0.1 microns;
- colloids – from 0.1 microns to 1 nm;
- dissolved particles.
Cleaning is done using different methods and means. Cleaning methods are divided into several groups:
- mechanical – filtration and hydrodynamic processes;
- physico-chemical – chemical and thermal treatment;
- biological - processing by bacteria.
When choosing a cleaning method and process, it is necessary to take into account the degree of contamination, content and size of impurities. Most often, for household (domestic) wastewater, biological and mechanical methods are used.
Video: Methods and facilities for wastewater treatment
Biological wastewater treatment
In nature, water is purified by microorganisms that live in it or the soil. Bacteria break down organic particles into gas and water. This method, although effective, is quite long.
Bacteria need an ideal environment for their life. For example, for aerobic microorganisms that require oxygen to function, aeration systems have to be installed.
But their brothers - anaerobic bacteria, do not need oxygen and cope well with their duties in sealed containers. It’s just that as a result of their work, gas is released, so for buildings in which these microorganisms are used, it is necessary to install a ventilation system.
Note! Biological wastewater treatment is used only after mechanical treatment.
Mechanical methods
Any wastewater treatment begins with sedimentation or filtration, due to which large impurities are removed from the liquid. For this purpose, coarse filters are used, such as sieves, gratings, sand traps, etc. Most treatment plants use a settling method in which heavier particles settle to the bottom, and lighter particles move to the next stage.
Note! During mechanical treatment, up to 65 - 70% of impurities are removed from household wastewater.
Chemical cleaning
This method is based on adding to the drains chemicals. As a result of the reaction that occurs during the interaction of chemicals with impurities contained in wastewater, a sediment is formed, which in turn is removed mechanically.
This method allows you to remove up to 25% of soluble and 95% of insoluble impurities. To disinfect water, potassium permanganate, chlorine and other substances capable of disinfection are used.

Physico-chemical method
For the purification and disinfection of domestic sewage, the physico-chemical method is rarely used. It is mainly used in wastewater treatment plants intended for the treatment of industrial wastewater.
Physico-chemical methods include:
- coagulation;
- flocculation;
- flotation;
- adsorption;
- ion exchange method;
- reverse osmosis method.
Since this technique is practically not used in, we will not analyze each point in detail in this article.
Methods used in domestic sewerage
Protozoa cleaning devices household sewer systems, which include cesspools, use two main methods in their work: mechanical and biological treatment. The wastewater in these devices is settled and treated by microorganisms.
Most conventional septic tanks use anaerobic bacteria in their work, that is, those that do not require air access. At the same time, purification occurs slowly, and the liquid is not completely purified, so at the outlet it is necessary to arrange additional purification - filtration fields.
More advanced treatment plants, in addition to sedimentation and anaerobic biotreatment, use inlet filtration and aerobic microorganisms. As a result, the output is 97-98% purified water.

Cleaning Standards
There are no strict requirements for household wastewater. Standards that specify permissible concentrations of a particular substance in purified water apply only to industrial treatment facilities. However, this does not mean that the untreated liquid can be poured into water bodies or directly onto the ground. For this they may be subject to administrative liability.
For household wastewater, the law regulates the concentration of certain substances if they are discharged into open water bodies. The same applies to water that is drained into the soil, since over time it will still end up in the reservoir.
Note! For efficient operation of the sewer system, follow the rules of its operation. You should not throw garbage into it, as well as pour out solvents, paints and varnishes, gasoline and other chemically hazardous substances. Only domestic waste should enter the sewer system.
Conclusion
There are many methods for treating wastewater; the choice depends on the nature of the contaminants and the requirements for the quality of treated water. Domestic wastewater is treated mainly mechanically and biologically. And the physico-chemical and chemical method is used in large enterprises.
Video: Modern technologies wastewater treatment
Mechanical method
It is usually used for preliminary or additional wastewater treatment (sedimentation, filtration).
Biological method
Organic contaminants are purified through the activity of various microorganisms living in wastewater. Depending on the conditions under which bacteria live, there are three possible options for the biological treatment process:
- Anaerobic conditions (without access to oxygen) are used in septic tanks and primarily remove phosphorus compounds.
- Aerobic conditions (oxygen blowing, so-called aeration) are used in aeration tanks and remove predominantly nitrogen compounds.
- Anoxide conditions (without aeration, but with oxygen in the composition of chemical substances) are usually created after aeration to further remove nitrogen compounds.
Compliance with all three conditions for the complete removal of all pollutants is technologically possible only in complex urban-scale treatment facilities. In local treatment plants, as a rule, one or at most two conditions are applied simultaneously, which, of course, does not provide the necessary degree of purification.
Chemical method
Wastewater treatment occurs through chemical reagents, usually coagulants, which convert dissolved forms of pollutants (primarily phosphorus compounds) into an insoluble sediment, which is removed along with excess sludge during the sewage disposal process.
Physico-chemical method
This method used for water disinfection at the final stage of purification: chlorination, ozonation, UV disinfection.
When choosing a local treatment plant, you need to take into account that any biological treatment station, be it a septic tank or an aeration tank, is capable of purifying wastewater only from organic contaminants, while other contaminants inevitably remain in the water and enter the soil or reservoir, accumulate and cause no harm. not only the environment, but also human health.
Therefore, to completely purify wastewater, it is necessary to use a comprehensive purification system that allows for maximum extraction of all pollutants from wastewater without additional devices.
To purify industrial wastewater, different wastewater treatment methods are used depending on its degree of contamination and composition. These wastewater treatment methods include: mechanical, chemical, physico-chemical and biological wastewater treatment methods.
In order to separate organic, insoluble mineral impurities from wastewater, mechanical wastewater treatment is used. This includes settling, filtration and straining. To complete the process of complete clarification of wastewater, you need to pass it (filter) through layers of granular material (expanded clay, sand or something else) with particles of various sizes. Most often, this treatment is used as a preliminary (but sometimes as a final) method for treating industrial wastewater.
When chemical reactions are needed to remove contaminants from wastewater, chemical treatment of industrial wastewater is used. During chemical wastewater treatment, the following occurs:
oxidation and reduction of impurities that are dissolved in water, and non-toxic or low-toxic products are obtained;
removal of alkalis and acids;
transformation into compounds that are insoluble in water.
One type of chemical wastewater treatment is electrochemical wastewater treatment - destruction harmful impurities, which are contained in wastewater through electrochemical oxidation at the anode or in the regeneration of valuable substances (iron, copper and others), which can be returned to production.
For physical and chemical methods of wastewater treatment, the following processes are used: coagulation, decontamination, sorption, ion exchange, extraction, evaporation, flotation, crystallization, dialysis, evaporation, deodorization and desalting.
Water coagulation is the process of transforming colloidal and dispersed particles into large ones, which occurs due to their gluing under the influence of molecular attraction forces. After coagulation is completed, flakes are obtained that are visible to the human eye. There are 2 known coagulation options:
coagulation in free volume (carried out in special reaction chambers or chambers where flakes are formed);
contact coagulation (in the thickness of the granular loading of contact clarifiers and contact filters or in the mass of suspended sediment from clarifier settling tanks).
In the process of sorption, organic substances and gases are released from wastewater by concentrating them on the surface of a solid (adsorption), or by absorbing compounds from a solution or a set of gases by liquids or solids (absorption), or by using the chemical interaction of substances that have dissolved, with a solid body (chemisorption).
Extraction is a method of separating substances into their component parts using a solvent in which they dissolve differently. The extraction process is carried out in special equipment called an extractor.
Evaporation is a method of purifying industrial wastewater using water vapor. Steam is passed through the heated wastewater, which collects volatile substances as it passes. The steam is then purified when it passes through a special absorbent substance and is used again to pass through the wastewater.
Flotation is the process of removing impurities from wastewater when a special substance is added to the water, which envelops the impurity particles and imparts buoyancy to these enveloping particles. For example, air is released into water, the particles stick to its bubbles. After this, bubbles with impurities rise to the surface of the water and here they can already be collected.
Ion exchange is the extraction of various cations and anions from aqueous solutions using ion exchangers - substances that are practically insoluble in water and in the body. solvents, or artificially made resins that are capable of ion exchange.
Crystallization is the purification of dirty water when contaminants are released in the form of crystals.
Dialysis is the release of colloidal solutions and solutions of high molecular weight substances from low molecular weight compounds dissolved in them using a semi-permeable membrane. During dialysis, molecules of dissolved low molecular weight substances pass through the membrane, and those that are unable to dialyze (pass through the membrane) colloidal particles remain behind her.
Deodorization - eliminating stench using chlorination, aeration and ozonation.
Desalting of industrial wastewater is carried out using ion exchange, evaporation, freezing and reverse osmosis.
Also, the crystal hydrate method of water demineralization is very interesting.
In order to use the method of crystalline hydrate wastewater purification, large energy and monetary costs are not required. The next advantage of the crystalline hydrate method of water purification is that scale does not form, since the temperatures are low (approximately equal to ambient temperature). There is also much less corrosion.
Often, when using wastewater treatment methods, which were described above, they expect to obtain valuable materials from these waters. Based on this, these wastewater treatment methods are classified as regenerative wastewater treatment methods. These methods are used when wastewater has greater concentration impurities.
There are also destructive methods of water purification. In destructive water purification, pollutants are destroyed using oxidation or reduction.
Destructive methods are used when wastewater contains organic impurities and does not represent any technical value. Also, destructive methods of wastewater treatment are used for post-treatment after regenerative methods of water purification. The main method, which is classified as destructive, is biological oxidation under anaerobic or aerobic conditions. After purification using this method, wastewater will meet sanitary and hygienic standards and can be discharged into water bodies. The cost of biological wastewater treatment varies depending on the substances that are included in the wastewater.
Joint mechanical treatment should be used if industrial wastewater pollution contains mostly organic substances that can be oxidized biochemically, and when special preparatory treatment is not necessary.
If biological methods of water purification do not satisfy the increased san. and fish farms standards, additional wastewater treatment is used. In these cases, the wastewater is subjected to thorough purification by one of the following processes: adsorption, filtration, flotation, ozonation, or some of them together.
Water purification by absorption is used more often in local treatment facilities. If a small amount is used activated carbon and provided that valuable substances are recycled, the water absorption method turns out to be cost-effective.
The electrochemical method of wastewater treatment is used in fixed structures for water purification. This method requires large amounts of electricity. The electrochemical method of wastewater treatment can be used if, as a result of purification, it is possible to obtain valuable substances and also where electricity tariffs are low.
Industrial wastewater that cannot be treated by the methods described above must be evaporated (for example, for desalting), burned (if the wastewater is very harmful and its treatment requires large financial costs) or pumped into deep layers that will absorb this water.
The choice of industrial wastewater treatment method depends on the quantitative and qualitative characteristics and local conditions. It is always necessary to use the simplest and most economical methods of wastewater treatment, as a result of which valuable substances can be obtained. As a result of the purification of industrial wastewater, a sedimentary product is obtained, which is sometimes quite valuable.
For organic sludge from industrial wastewater that cannot be disposed of, incineration is used. Usually dehydrated sludges, which contain oil waste and organic extractants, are burned.