In construction, synthetic materials are successfully replacing metal: they are on average cheaper, more durable (since they are not subject to corrosion), easier to install and lighter. Let's look at what polypropylene pipes are - technical specifications, types, application features.
There are three types of polypropylene for pipes:
- homopolymer (PPH);
- copolymers (PPV);
- static copolymer with ethylene (PPRC), also known as random copolymer. Ethylene provides high thermal stability. Polypropylene pipes and heating fittings of this type can withstand temperatures up to 110º for a short time. They are used most often.
The physical and mechanical characteristics of PPR are regulated by existing standards:
- in accordance with GOST 21553, the melting point of the material is + 149º;
- according to GOST 15139, PPR density is 0.9 grams per cubic centimeter;
- according to 11262, tensile strength (yield strength) is 24-25 N/sq.mm, elongation when it is reached is 50%:
- tensile strength – 34-35;
- according to 15173 coefficient of thermal expansion – 0.15 mm per mms;
- for 23630 specific heat capacity – 2 kJ per kgf (at +20º);
- according to DIN (German standard) - thermal conductivity 0.24 watts per m/s (at +20º).
The advantages of PPR pipes include:
- non-susceptibility to corrosion and rotting, high durability (for heating and hot water pipes - 50 years, for cold water supply - 100);
- sediment does not collect on the walls, which often “overgrows” metal pipes. Over time, the diameter of the internal channel does not change;
- the cost is lower than that of metal products;
- the weight is on average 9 times less than that of metal ones of the same section;
- simple and inexpensive repair. Polypropylene does not need to be painted regularly; replacement of damaged components is carried out without expensive equipment;
- sections of pipes are connected to each other by welding (the so-called “iron” for polypropylene). The connections are permanent and extremely reliable. Quantity threaded connections(through which leaks most often occur) in the system is minimized;
- plastic has low thermal conductivity: heat loss through the walls and condensate accumulation on the pipes are minimized;
- sound insulation (as opposed to sound-conducting metal pipes);
- due to the plasticity of the material, the pipes do not burst when the coolant freezes in cold weather;
- high chemical resistance;
- environmental cleanliness;
- non-susceptibility to fungal infections;
- the material is supplied in coils that are convenient to transport.
Areas of application
Where can polypropylene pipes be used:
- main application - water supply and (depending on the characteristics) heating systems;
- sewerage systems;
- transportation of chemicals, including aggressive ones;
- pipelines with the highest strength characteristics can be used to transport compressed air;
- in irrigation and land reclamation systems, for drainage installations.
Important: When installing boiler heating in a private house, the sections of the pipeline immediately adjacent to the boiler, as well as the gas supply hose and the chimney, are made strictly of metal pipes.
The area of use depends on the specific model of polypropylene pipe - the main parameters, material of manufacture, presence or absence of reinforcement. The main technical characteristics of sewer polypropylene pipes are the maximum permissible temperatures and pressures for the pipeline for drinking water increased sanitary requirements etc.
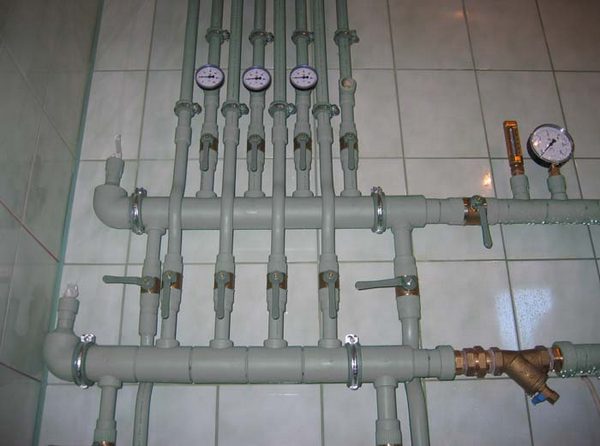

Types, markings, characteristics
The technical characteristics of polypropylene pipes for water supply are different. First of all, the resistance to high pressures and temperatures. The possibility of application for certain purposes depends on these parameters.
Main types of polypropylene pipes and their characteristics:

Note: At the moment, you can find on the market not only polypropylene pipes marked PN 25, which have reinforcement.
The colors of polypropylene pipes of all types are gray, white, green and black. For blacks better protection from ultraviolet rays, otherwise color does not affect the characteristics of polypropylene pipes and fittings for water supply or other systems.
Types of fittings
A fitting for polypropylene pipes is a connecting element also made of polypropylene. May have a nickel-plated brass pressed insert with thread. The following connecting parts are used for the installation of pipelines:
- coupling - a hollow element similar to a miniature barrel for welding pipes of the same cross-section. Pipes are inserted from both sides;
- adapter - a similar element, but for connecting pipes with different diameters. There are also adapters for connecting plastic pipes with metal ones, with threads at one end;
- the corner is used to turn the highway: this way you can avoid unnecessary bending. There are angles at 45 and 90 degrees, as well as those combined with adapters - with different cross-sections of inlet holes, with metal threads on one side;
- tees and crosses are used to connect more than two pipes. The angles and configuration are different, there are parts with and without threads;
- bypasses - parts for bypassing structural elements (for example, other pipes). Allows you to avoid unnecessary bending of polypropylene. Shapes and sizes vary;
- compensators. They exist in finished form, but if necessary, can be assembled from fragments of pipes and corners;
- American - dismountable fitting, coupling with union nut. In those areas that will be periodically dismantled (to clean the unit, install a water meter, etc.), it is preferable to install an American one.
In addition to connecting parts, the pipelines use faucets and valves made of polypropylene, plugs (to cover blind end sections), fasteners and clamps for mounting on walls.

Connection Features
Three types of welding are used to connect polypropylene pipe sections:
- end-to-end;
- polyfuse (bell-shaped);
- using electrical fittings.
When connecting to metal pipes, fittings with threaded inserts are used. Teflon tape and other sealants are used to seal joints.
Important: You cannot cut threads on factory products yourself. For installation, you should use fittings and pipes of the same brand; this is the only way to guarantee the quality of the finished system.
Several basic rules for installing a sub-pipeline:
- Before starting work, you need to carefully inspect the material to avoid damage and contamination.
- Installation should be carried out at a positive temperature of 5 degrees, if necessary, bend pipes - from 15.
- The maximum bending radius depends on the size of the pipes. For example, for 1.6-3.2 cm - 8 diameters.
- Fastening is carried out taking into account thermal expansion. When heated, the pipe becomes deformed and may burst. Installation on a fixed support is only permitted for a short distance. In all other cases, a movable one is used, allowing for the possibility of compensatory displacement without deviation from the axis of the pipeline.
- The required slope of the pipe is from 0.5 percent towards draining the coolant or water using a drain tap.
- Wall bends are mounted on a rigid plate to eliminate torsional stresses.

Popular manufacturers
Brands of pipes and fittings popular today on the Russian market:
- Valtec (Italy) presents three categories of polypropylene pipes: thin-walled, foil-reinforced (99.4% aluminum), fiberglass-reinforced. Material – PP-R 100. The layers are glued with adhesives made in Japan and America, providing a layer strength of 70 N per 10 mm (standard – 15). During the welding process, a bead of straightened plastic does not form. A special feature of the fittings is a conical socket. Parts with metal threads are octagonal (due to their shape, they can be worked with standard keys).
- Banninger (Germany). The raw material is chemically neutral polypropylene random copolymer. The products can also be used to supply drinking water. The main disadvantage of the brand is the high price.
- Wavin Ecoplastic (Czech Republic). The pipes can withstand loads of up to 20 atm. Types of heating pipes: Stabi - foil reinforced, Fiber, Basalt+ - basalt fiber. The remaining models are suitable for cold water supply.
- Kalde (Türkiye). Types: pure polypropylene – PN10 and 16; glass fiber reinforced – PN16; superpipe – reinforced with perforated aluminum foil. The latter type does not require stripping and facing when welding. Service life at temperatures up to 70 degrees is 50 years.
- Tebo (Türkiye). The raw material is a durable polymer of the new generation Random Copolymer (PPR of the third type). Products have certificates for compliance with DIN, GOST, TSE standards. Section sizes are from 2 to 16 cm, types of pipes are PN10, 20 and 25. The foil in PN25 is non-perforated; stripping is required during welding.
- SPK (Türkiye). Polypropylene pipes are on average half the price of European brands, while maintaining high quality. Manufactured from Dutch raw materials using German equipment. Excellent characteristics: the products can also be used in difficult operating conditions (for example, in Siberia).
Plastic communications are increasingly used for the construction of sewerage and water supply systems. Polypropylene pipes for heating and plumbing are very popular.
Polypropylene is a material obtained by polymerization of propene, abbreviated as PPR (PPR). Thanks to special processing, this plastic is very light, but at the same time, it is not inferior in strength to PVC compounds. Such pipes are used to heat the greenhouse, install heated floors, and provide heat and water supply.
Technical characteristics of polypropylene:
- Density: 0.91 kg/cm2;
- Resistance to sudden temperature changes;
- Operation in the temperature range from -15 to +110 degrees. At the same time, manufacturers note that polypropylene begins to melt at a temperature of 140 degrees Celsius, and the maximum permissible temperature in heating networks is 120;
- The coefficient of thermal linear expansion is 0.15 mm/m*C. This is the lowest among all types of plastic products. It means that when exposed to high temperatures, the pipe lengthens by more than 15%. This change can lead to irreversible damage to heating communications, ruptures of pipelines and depressurization of the system.
- Polypropylene is a very soft material; soldering and glue are suitable for joining it. The system can also be cooked using gas;
- Polymer plastics are considered the safest among all materials used for installing water pipes. The water after them does not change its odor and natural composition, and is not contaminated with salts (which often settle in the middle of metal communications) and microorganisms.
Polypropylene and metal-plastic pipes, fittings (facing), manifold and other components must be correctly selected according to the operating pressure in the system in which they will be used. For example, heated floors often use the simplest PN 16 or 10 (they are easy to bend); in order to connect the heating circuit, reinforced PN 32 (marked PPBBPP) is needed.
 Photo: polypropylene fasteners
Photo: polypropylene fasteners Table of use of polypropylene pipes PN 25, 32 GOST 24157-80 and others:
| Operating temperature, degrees Celsius, C | Service life | Type of pipeline | |||
| PN 16 | PN 20 | PN 25 | PN 32 | ||
| Pressure, kgf/cm 3 | |||||
| 20 | 10 | 21,7 | 27,1 | 33,9 | 34 |
| 25 | 21,1 | 26,4 | 33 | 33,7 | |
| 50 | 20,7 | 25,9 | 32,3 | 33,2 | |
| 30 | 10 | 18,8 | 23,5 | 29,3 | 30,06 |
| 25 | 18,1 | 22,7 | 28,3 | 29,1 | |
| 50 | 17,7 | 21,1 | 27,7 | 28,5 | |
| 40 | 10 | 16,2 | 20,03 | 25,3 | 26,2 |
| 25 | 15,6 | 19,5 | 24,3 | 24,8 | |
| 50 | 14,7 | 18,4 | 23 | 24 | |
| 50 | 10 | 13,9 | 17,3 | 21,03 | 21,5 |
| 25 | 12,8 | 16 | 20 | 21 | |
| 50 | 11,7 | 14,7 | 18,3 | 19,8 | |
| 60 | 10 | 11,5 | 14,4 | 18 | 19,3 |
| 25 | 9,8 | 12,3 | 15,3 | 16,5 | |
| 50 | 8,7 | 10,9 | 13,7 | 14,8 | |
| 70 | 10 | 8,5 | 10,7 | 13,3 | 14 |
| 25 | 7,3 | 9,1 | 11,3 | 12,3 | |
| 50 | 7 | 8,8 | 11 | 12 | |
| 80 | 10 | 6,8 | 8,5 | 10,7 | 12,5 |
| 25 | 6,9 | 8,7 | 10,8 | 11,5 | |
| 50 | 6,3 | 7,9 | 9,8 | 10,9 | |
| 95 | 10 | 5,9 | 7,5 | 9,2 | 10,5 |
| 25 | 6,7 | 7,6 | 8,5 | 9,7 | |
| 50 | 4,4 | 5,4 | 6,1 | 7,03 | |
When choosing compression fittings or compensators for polypropylene pressure pipes, you need to ensure that their operating pressure is higher than in heating or water supply systems.

Types of polypropylene pipes
Due to significant disadvantages (high expansion rate), these communications were rarely used in heating systems. In particular, in those areas where the temperature did not drop to -25 degrees, or the scheme provided for the use of metal connections. But this is impractical, because this type of plastic is considered the lightest and most flexible of all that can be used for water supply installations.
Types of pipelines:
- Glass fiber reinforced polypropylene pipes;
- Regular communications.
If conventional connections were most often used for cold water supply, then for heating systems or connecting a boiler hot water– reinforced. They can withstand temperatures up to +120–130 degrees, while expanding by a minimum amount. Reinforcement with aluminum and fiberglass made it possible to reduce the elongation coefficient to 0.03%.

Reinforcement also comes in different types:
- Internal;
- Middle.
The internal type of reinforcement is most often carried out with a solid sheet of aluminum. It is attached to the pipe and helps ensure its strength and high density. At the same time, the communication becomes more difficult to bend, which makes it much more difficult to install reinforced polypropylene pipes with your own hands. In addition, salts and mineral compounds can accumulate on the aluminum layer, which can later cause a pipeline blockage.
Video: Polypropylene pipes - how to choose.
More often used for heating systems are polypropylene reinforced pipes with threads or aluminum wire in the middle. This reinforcement is located between layers of polymer, which ensures that there is no possibility of communication clogging. Often the wire is placed between several polymer spaces - this helps to increase rigidity.
Installation
Soldering RVK sewer and heating polypropylene pipes is no more difficult than any other plastic ones. There are certain rules by which the system must be connected. Step by step instructions how to install a sewer frame:
- To get started, you need to prepare the tool. This is a welding machine for polypropylene connections (inverter or hand soldering iron), scissors for cutting pipes, connections (American fitting, gaskets, union, etc.);
- First, the connections are cleaned. The pipe cutter presses against the desired section of the communication and cuts it to the required dimensions. Please note that depending on how you solder the joints, you may need to cut and clean one side and thread the other;
- Afterwards you need to make a chamfer, it is made at an angle of 15 degrees;
- To smoothly connect the pipes together, a trimmer is used. Before soldering the communications, make sure that they are perpendicular to the floor. To do this, you need to install them in a centralizer and connect them;
- Welding is carried out at a certain temperature. Many manufacturers of welding machines for plastic indicate in the instructions what temperature will be optimal;
- It takes a certain amount of time to weld polypropylene pipes so that diffusion occurs, but the plastic does not overheat. Afterwards, it is warm and left in a vice to cool.
The technology for heating polypropylene pipes can be different depending on their purpose. Sometimes attachments are mounted on equipment, for example, electrical couplings. They will help to warm up the connection at the desired point, without affecting other areas of the craft.

Thus, you can carry out not only home-made installation, but also repair cracked pipes or eliminate depressurization of the system. Then welding or soldering of polypropylene reinforced pipes is carried out using special sealants.
Price overview
You can buy polypropylene pipes at any plumbing supply store; the price is determined by the number of communications and geometric data (dimensions of length, thickness and diameters). The choice is very large, both domestically produced and imported. Good reviews about the products of Valtec, Banninger, Dytron, Kalde, Pro Aqua, Euroconus, Fv-Plast (Czech Republic).
Let's consider how much a linear meter of PN 20 pipe costs:
Sales are carried out both wholesale and retail. You can also immediately buy a set of fasteners and adapters (if you plan to combine metal pipes and plastic).
Perhaps the most important development in the field of plastics technology is the invention of high-temperature polypropylene. The resulting copolymer, which belongs to thermoplastics, is characterized by high strength and low weight. In addition, polypropylene is not afraid of most alkaline and acidic solvents.
Polypropylene pipes are quite versatile in terms of transporting liquid, the temperature of which can range from -10C to + 90C, while the temperature can briefly rise to +110C. A polypropylene pipe can even withstand freezing of the liquid in it.
Main characteristics of polypropylene pipes
- Density: 0.9 g/cu.m. cm (according to GOST 15139);
- Melting point: +149C (according to GOST 21553);
- Tensile strength: 34-35 N/sq.mm (according to GOST 11262);
- Yield strength (tension): 24-25 N/sq.mm (according to GOST 11262);
- Expansion coefficient of polypropylene pipes: 0.15 mm/mmС (according to GOST 15173);
- Elongation at yield point: 50%;
- Specific heat capacity (at +20C): 2 kJ/kgf (according to GOST 23630);
- Thermal conductivity (at +20C): 0.24 W/ms (according to DIN52612);
Types of polypropylene pipes and their areas of application
At the moment, all manufactured pipes are divided into 3 main categories. The first two types (PN10 and PN20) are made of monolithic material, and the third (PN25) is produced with an aluminum alloy layer. There is also an intermediate category - PN16, which is universal, suitable for installing hot and cold water supply at a pressure of 1.6 MPa.
- PN10 is a thin-walled pipe used for installation of cold water supply systems (up to +20C), heated floors with coolant temperatures up to +45C. The nominal operating pressure for this pipe is 1 MPa (10.2 kg/sq.cm). The dimensions of polypropylene pipes of class PN10 are standardized: the outer diameter of the pipe is 20-110 mm, the inner diameter is 16.2-90 mm. Wall thickness 1.9-10 mm.
- PN20 is a universal option. Can be used in hot water supply systems with water temperatures up to +80C and pressures up to 2 MPa (20.4 kg/sq.cm). The outer diameter of pipes of this class ranges from 16 to 110 mm, the inner diameter is 10.6-73.2 mm. Wall thickness 16-18.4 mm.
- PN25. Pipes of this category are reinforced with a layer of aluminum foil. Designed for installation of central heating systems with coolant temperatures up to +95C, as well as hot water supply systems. Nominal pressure – 2.5 MPa (25.49 kg/sq.cm). The reinforcing layer is located closer to the outside of the pipe. In this case, the use of glue in the production of the pipe is not required, due to the perforations on the foil. This also increases the strength and stability of the pipe. Pipes of this class can also be used in cold water supply systems. The outer size of PN25 class pipes is 21.2-77.9 mm, the inner size is 13.2-50 mm. Wall thickness 4-13.3 mm.
The appearance of PN25 class pipes helped to partially solve the problem with the high coefficient of thermal expansion of polypropylene pipes. There are also certain disadvantages of this pipe, for example, the complexity of its installation and connection with fittings, since this requires a welding nozzle or a special end cutter.
Not long ago, a new type of pipe was developed, which consists of three layers. The middle layer in this pipe is a mixture of fiberglass and polypropylene. At the same time, the thickness of the new polypropylene pipe remained unchanged.
The new glass fiber pipe has a very low expansion coefficient of only 0.009 mm/mt (C). Also, the tensile strength of fiberglass is 2 times higher than that of steel. The result is a product that is easy to install and has a lower coefficient of thermal expansion.
Polypropylene pipes can be grey, white, black or green, which does not affect their technical properties. Only black polypropylene has higher UV protection.

Advantages of polypropylene pipes
The main advantages of these pipes include long term operation. However, it is only possible if the manufacturer’s recommendations for the use of a specific type of pipe (PN10, PN16, PN20, PN25) are followed. At the same time, pipe manufacturers claim that these products can last at least 50 years, and in cold water supply systems up to 100 years. Moreover, short-term increases in pressure and temperature have virtually no effect on the service life of polypropylene pipes.
Those parts of pipelines that are in direct contact with drinking water, are in full compliance with the standards of Russia, Germany, USA, Belgium, Italy, England, Spain. These are not all the advantages of polypropylene pipes:
- On inner surface, which is in direct contact with water, no deposits, such as corrosion, are formed. As a result, the internal diameter of the pipe does not decrease over time;
- The good sound absorption of the pipe allows you to dampen the noise that usually occurs when transporting coolant or water;
- PPR type polypropylene resists sudden changes in pressure and temperature well. The appearance of condensation on the pipe is excluded, since it has low thermal conductivity;
- The relatively low weight of these pipes makes them easier to transport (the weight of a polypropylene pipe is approximately 9 times less than similar metal products). This moment also facilitates the installation process, because only one or two people will be enough;
- The time spent on installing these pipes is lower compared to installing metal analogues, and welding technology allows you to make connections of polypropylene pipes with high quality and quickly;
- These pipes require virtually no maintenance, they do not need to be painted, because they have an even color along their entire length;
Fittings for polypropylene pipes
For polypropylene pipes, manufacturers offer various types fittings necessary for the installation of any engineering communications. The use of fittings eliminates the need to use metal parts.

Using special couplings, you can reliably connect a polypropylene pipeline with a metal one, and fittings with chrome and brass inserts greatly facilitate the process of connecting pipes to various plumbing fixtures.
Immediately before installation, the pipe must be carefully inspected for damage or contamination. The temperature in the room where the pipes are installed should not be lower than +5C, otherwise all connections may not be of very high quality. Pipes can be bent without using heat only at an air temperature of at least +15C. In addition, the maximum radius of 8 diameters for a pipe with a diameter of 16-32 mm cannot be exceeded.
By welding, you can obtain a homogeneous seam, which will ensure a high quality connection. There are three types of welding:
- Butt;
- Polyfuse;
- Using electrical fittings;
There are also special fittings that have threaded inserts. To seal threaded connections, various sealing materials are used, for example, special Teflon tape. It is worth remembering that you should not cut the thread yourself, since in this case no one will guarantee the quality of the connection of plumbing fixtures and pipes. It is best to purchase fittings from the same manufacturer as the pipes.
When fastening pipelines, you must not forget about their thermal expansion. Typically 2 types of fastening are used:
- A movable support in which the pipeline has the possibility of compensatory movement, i.e. stretching and compression. The pipeline does not deviate from the route axis;
- A fixed support that does not imply the possibility of compensating for the movement of the pipeline along the axis. This type of support is only suitable for short sections of the route, since the pipe may burst due to expansion when heated;
In addition, you need to ensure that the slope is maintained (at least 0.5%) towards the lowest places where it is possible to drain the coolant using taps. When installing water-folding equipment, do not allow torsional stresses on the wall elbows, which should be secured to a rigid plate that ensures their stationary position.
Polypropylene products belong to the group of environmentally friendly pure materials. They are more attractive than steel products of lower cost and weight, and are superior to metal-plastic options in strength and durability. Parts marked PN 20 have a wider range of applications, so they are more in demand compared to other options on the market. Let's take a closer look at the technical characteristics of the PN 20 pipe, the properties of the material, its pros and cons.
Features of the material
The material from which the PPR PN 20 pipe is made is random polypropylene copolymer (third type). It was invented relatively recently, which made it possible to use products in high-temperature conditions. The main features of the material include:
- High resistance to direct exposure to acidic and alkaline solvents.
- High plasticity, thanks to which products easily tolerate freezing and thawing of moisture inside them.
- The temperature range for using parts made from this material has been expanded – from 10 to 90˚С.
- The material is absolutely non-toxic, therefore it is successfully used for assembling drinking water supply systems.
- When processing and recycling parts, no environmentally harmful substances are released.
All these distinctive features were obtained by adding ethylene molecules to the polypropylene molecular chain. By modifying its structure, the indicators of ductility, viscosity and temperature strength were improved.
For self-installation system, you will need to purchase a special welding machine. The connection of segments using it is most hermetically sealed and reliable.
Varieties
The pipe in question, marked PN 20, is produced by manufacturers only in a single form and does not have any variations. But you can often hear about purchasing or using reinforced pipe PN 20. In fact, this type of product is produced under a different marking - PN 25. It received the status of a reinforced analogue by mistake, since the external parameters of the products are the same.
The wall thickness of the pipes under these markings will be the same for all existing diameters, but their weight will vary. The heaviest parts are those with an aluminum reinforcing layer, those of medium weight are those with a layer of fiberglass, and the lightest are those that have no reinforcement at all.
The pipes also differ in the maximum permissible temperature of the working medium and operating pressure. So for PN 20 models the permissible temperature is not higher than 80˚C. For parts reinforced with glass fiber, this figure is higher – 95˚C. For parts reinforced with aluminum, short-term exposure to a coolant with a temperature of 100˚C is allowed. The maximum working pressure for unreinforced models is 20 atmospheres, and for reinforced ones - 25 atmospheres.
Scope of application
PP PN 20 pipe is used for various purposes.
- As a distribution water supply mechanism in residential, industrial, administrative buildings and agro-industrial complexes.
- For laying water supply (hot and cold) indoors and outside buildings.
- For installation of “warm floor” systems, which are laid in niches under the floor covering, or embedded in a concrete screed.
- As connecting segments for connecting radiators to the heating system.
- For distributing a heating system in rooms where the maximum temperature does not exceed the permissible value for the material used.
- For connecting heating systems to boiler systems.
- As systems transporting compressed air or aggressive chemicals.

Do not bend the products. All turns are performed strictly at right angles using adapters and couplings.
Specifications
The marking is deciphered as follows: PPR - polypropylene rand (improved third type), PN - nominal pressure. Technical characteristics of PPR PN 20 pipe:
- Linear expansion coefficient (1/˚С) – 12.7*10-5.
- Thermal conductivity coefficient (W*m/˚С) – 0.238.
- The maximum permissible temperature is 80˚С (to increase the service life of products, it is recommended not to exceed 70˚С).
- The maximum permissible pressure is 2 MPa (1 MPa = 10 atmospheres).
- The wall thickness with a product diameter of 20 mm is 3.4 mm.
- The weight of one meter of a product with a diameter of 20 mm is 170-175 g.
Product advantages
The choice of PN 20 pipe is influenced by its many positive qualities. We list the main advantages:
- Lower cost and weight compared to traditional ones metal products.
- Simple and fast system installation process. Socket welding reliably and hermetically connects the segments (it takes 10-15 seconds to heat the parts).
- The elasticity of the material allows the products to be used for assembling underfloor heating systems and laying plumbing in unheated areas.
- The material from which the parts are made is non-toxic and resistant to chemical attack.
- The inner walls are resistant to corrosion, and the smooth surface prevents the formation of plaque.
- Resistant to temperature changes and pressure surges.
- The low thermal conductivity of the material eliminates the risk of condensation forming on the surface of the system.
- High level sound insulation reduces the noise level of the system.
- Resistance to aggressive environments, which reduces the cost of additional protective measures (painting, priming and other procedures).

The service life of parts in a heating or hot water supply system is 25 years. The service life of parts in a cold water supply system is twice as long
Technologically correct installation of the system, quality connection its segments between each other and compliance with operating rules will significantly increase the service life of the water distribution mechanism.
Progress does not stand still: these days massive steel pipes ceased to be in demand, and in their place came reinforced polypropylene pipes or, more simply, plastic pipes. These products are convenient to store, transport and install, which is an important advantage for every craftsman, from beginner to professional.
General properties and scope of application
Let's look at the technical characteristics of polypropylene pipes. How do they stand out among similar products made from other materials?
Main advantages:
- polypropylene products are cheaper than their steel counterparts;
- low weight of polypropylene pipes;
- the service life of polypropylene pipes reaches 50 years;
- no need for special care (there is no need to paint them or treat them in any way (it is enough to wipe them occasionally with a damp cloth to remove dust);
- with the help huge selection fittings, it is possible to design a wiring system of any complexity;
- corrosion resistance;
- minimal possibility of pressure loss;
- high throughput;
- safety of the material (environmentally friendly non-toxic type of plastic);
- During long-term operation, no layers are formed on the inner surface of the product.
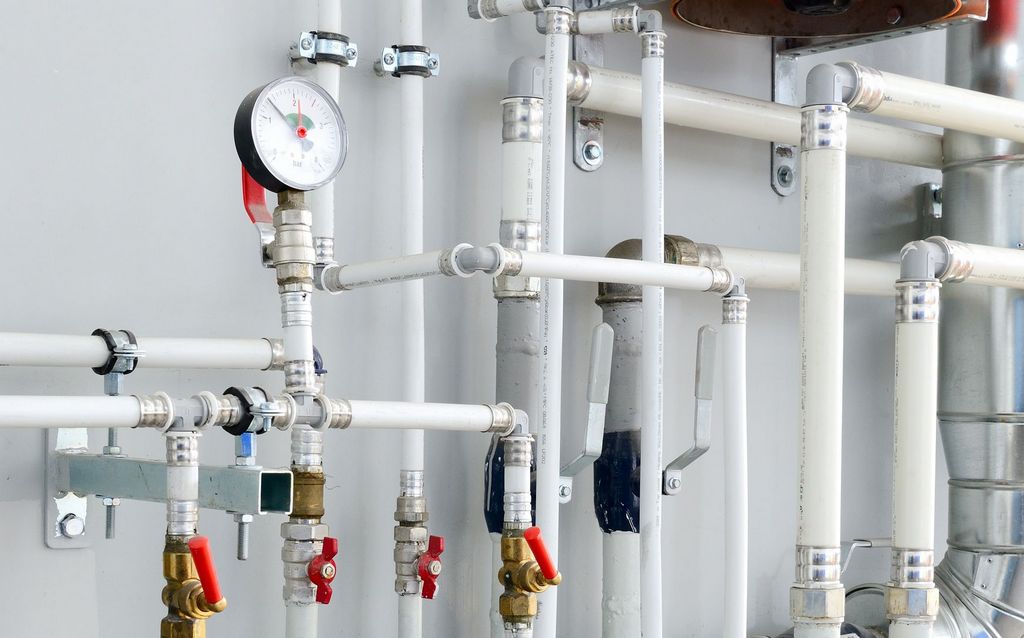

Scope of application:
- hot and cold water supply;
- water heated floor system;
- central heating wiring;
- drinking water supply;
- sewerage;
- ventilation systems.

Polypropylene pipes have characteristics sufficient for transporting (in the pipeline system) compressed air and chemically active liquids. Thus, there are practically no restrictions in the operation of polypropylene pipes; you just need to select the right type, relying on the designation and labeling.
Classification and technical characteristics
Types of polypropylene pipes are divided into single-layer and multi-layer. The classification of polypropylene pipes is more complex and is divided into chemical composition, structure and diameters. The area of use and the overall service life of the products depend on all these parameters.
Single layer products
According to the manufacturing method and material, single-layer polypropylene pipes are divided into several types:
Type 1 – PPH. Material – homopolypropylene. High levels of hardness and bending resistance combined with low resistance to increased and low temperatures determine the scope of their application: communications made of homopolypropylene are widely used in cold water supply and ventilation systems.

Type 2 – PPB – polypropylene block copolymer. An improved chemical structure with a polyethylene additive improves the heat resistance and flexibility of the material. This type of product is used for the installation of underfloor heating systems, cold water supply, ventilation and sewerage; it is not suitable for hot water supply due to the large thermal expansion of the material.

Type 3 – PPR – random copolymer of polypropylene, they are also called polypropylene pipes and are designated PPRC. It is distinguished by increased resistance to high temperatures and the effects of acids and alkalis, and is even superior to metal-plastic in strength. A product made from such a material is universal, and its scope of application is very wide, but its main purpose is heating systems. Polypropylene pipes have the following technical characteristics:
- absolute environmental friendliness;
- slight thermal expansion;
- high melting point (+170 °C);
- ability to withstand temperature changes at maximum values up to +130 °C;
- frost resistance;
- high constant operating temperature (90°C).

Type 4 – PPS – special low-flammable polypropylene, capable of withstanding temperatures up to 95 ° C in constant operating mode.
Brands of single-layer pipes
Single-layer polypropylene products can be divided into several categories, differing in their technical characteristics and permissible operating pressure.
- PN10 is a thin-walled model, designed for cold water supply (up to 20 °C), installation of heated floors (up to 45 °C), as well as for a ventilation system.
The dimensions of polypropylene products of this type are presented in the table:

- PN20 is a universal type of product intended for cold and hot water supply (up to 80°C).
For convenience, the parameters of the product of this brand, including the outer and inner diameter and wall thickness, are presented in the table:
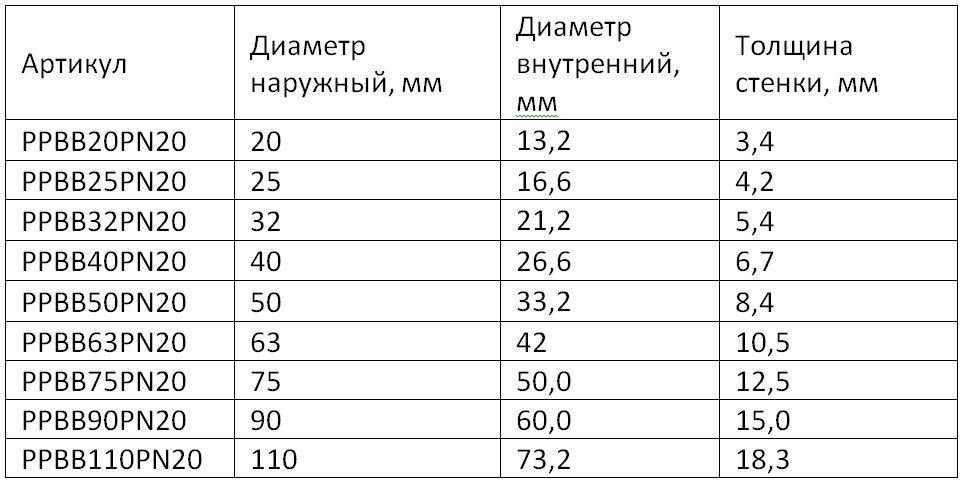
- PN16 is an intermediate model. Used less frequently than others, intended for cold and hot water supply (up to 60°C).
Multilayer polypropylene pipes
As is clear from the name, this type of pipe has 3 layers firmly bonded to each other. The middle layer may consist of aluminum foil, polyethylene or fiberglass. This product is marked PN25.
Models with aluminum core
Polypropylene pipes reinforced with aluminum Pn25 are used primarily for installation of heating system wiring, although they are also used for laying cold and hot water supply systems. Polypropylene products of this class are the most popular among plumbers.
The aluminum layer in the PN25 pipe can be smooth or perforated. As practice shows, a smooth aluminum layer is not very convenient, since it needs to be cleaned before welding so that the aluminum does not come into contact with water or other media that will be transported. The perforated layer in PN25 products is more practical: it is a mesh with holes into which molten polypropylene flows during the welding process, which makes the bonding more reliable and safe.

Products with a polyethylene layer
Polypropylene pipes with an internal polyethylene layer have many disadvantages. For example, when welding, only the outer layer is connected to the fitting, which means that the inner layer will come into contact with the transported media.
Glass fiber reinforced pipes
The most prominent type of product in this classification is glass fiber reinforced polypropylene pipes. A visual feature of this type of product is the tinted layer with fiberglass - this is done so that it can be distinguished from other types. There are many advantages to such products:
- due to the internal fiberglass layer, the pipeline elements become more rigid and turn into a monolithic structure;
- the coefficient of thermal expansion is almost 2 times less than that of non-reinforced products;
- high strength;
- ability to retain its properties at high temperatures;
- protection from water hammer;
- best throughput.

The markings of polypropylene heating pipes of different diameters are presented in the table:
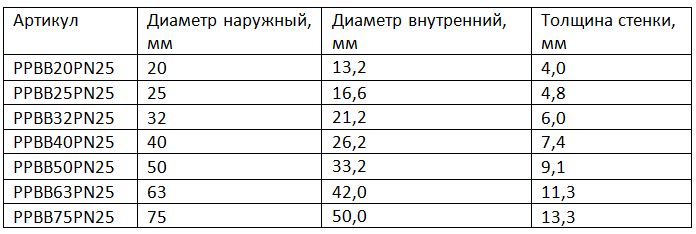
The type of product PN25 must be selected for a specific type of water supply or heating, taking into account the characteristics of operation. When choosing, you need to consider the following technical characteristics:
Pipe selection: what to look for
- The internal or bore diameter of polypropylene products is the most important value that you need to rely on when choosing pipes and fittings for them.
The standard outer diameter of products for a centralized heating system is 25 mm and 32 mm, the inner diameter is 16.6 mm and 21.2 mm, respectively. You can connect the radiator using a pipe with diameters of 20 mm (external) and 13.2 mm (internal). For heated floors, products with an internal diameter of up to 16 mm are suitable. For plumbing in an apartment, pipeline elements with a diameter within 20 mm are usually selected. A 40 mm polypropylene pipe is used for heating and water supply risers, and a 63 mm polypropylene pipe is used for routing lines in technical rooms.