It is very difficult to name those areas in which steel pipes are not used. They are used in oil pipelines, heating mains, main water pipelines, heating systems and many others. Many people are interested in how long a steel pipe can last. Their service life depends greatly on operating conditions.
How long can steel heating pipes last?
A heating system that uses steel pipes has always been considered durable and reliable, capable of withstanding fairly heavy loads. Service life steel pipes heating is thirty years. But why do some owners of newly built houses refuse steel pipes and prefer to make heating from plastic? The whole point is that the pipes are chosen incorrectly. There are two types of steel pipes:
— suture. This is the cheapest type of steel pipe. The choice of this type of pipe for heating is doomed to failure in advance, since its service life is only a few years and they will not live up to thirty years. This is because when installing a heating system, it is very difficult to bend such a pipe and the seam simply bursts at the bend. Also, the inside of the seam cannot be properly processed; a leak may appear and the pipe will need to be replaced. Therefore, it is not suitable for heating systems;
— seamless. Such pipes are much more reliable. For individual heating, such pipes with a diameter of 25 mm are recommended; when tested, they can withstand loads of up to 20 atmospheres. Therefore, for at least twenty years, such pipes will last without problems.
Remember that previously only steel pipes were installed for the heating system. And often, when installing autonomous heating and replacing steel pipes with plastic ones, it turned out that they could serve for a long time, despite the fact that they were installed twenty years ago.
How long can steel water pipes last?
 Service life of steel water pipes and sewer pipes made of the same metal are fifteen years old. The same galvanized steel pipes can last for thirty years. During the first five years of operation, the inner surface of the water supply pipes becomes overgrown, and wet condensation appears on the surface, not to mention the fact that they withstand large dynamic loads. And galvanized steel pipes are coated with an anti-corrosion coating, so they can last much longer.
Service life of steel water pipes and sewer pipes made of the same metal are fifteen years old. The same galvanized steel pipes can last for thirty years. During the first five years of operation, the inner surface of the water supply pipes becomes overgrown, and wet condensation appears on the surface, not to mention the fact that they withstand large dynamic loads. And galvanized steel pipes are coated with an anti-corrosion coating, so they can last much longer.
Advantages and disadvantages of steel pipes
 Advantages:
Advantages:
- low cost, however, this is compensated by high cost installation work;
- strength;
— with increasing temperatures there is slight deformation;
- durability.
Flaws:
— corrosion. However, to delay it, a zinc coating is used, which is found on galvanized pipes, which can last the longest;
— to work with pipes, welding is required;
- do not bend well;
— with a sharp increase in pressure, the pipe may rupture.
Without pipes it is impossible to imagine the life of not only an individual home or business, but also entire districts and cities. Pipes are used to move cold and hot water, for creating heating mains, sewerage systems, for many other purposes. Not only their service life, but also the ecology of both an individual section and the country as a whole depends on the quality of pipes.
The length of networks (in single-pipe measurement) in Russia is impressive - it is more than 1 million km! At the same time, about 30% (!) of pipelines are so worn out that they need urgent replacement and repair.
Let's take a closer look different types pipelines (water supply, heat supply, sewerage), their condition and problems arising due to their wear and tear and poor quality.
Water supply pipelines
The total length of water supply networks is more than half a million km and approximately 30% of them need replacement and repair. What are the dangers of old steel pipelines overgrown with rust?
Firstly: with leaky pipelines, it is impossible to ensure the supply of water from its intake to the tap without reducing the quality. Contamination of water during its transportation occurs both due to corrosion products and as a result of suction groundwater through leaks. Polluted water worsens health and affects the life expectancy of every Russian at the genetic level.
Secondly: overgrowing inner surface pipelines entails an increase in the energy required for pumping. The internal surfaces of approximately 80% of water pipes have such deposits that they throughput compared to the design one it decreases by 2-2.5 and even 3 times! According to calculations by the Academy of Public Utilities, overgrowing of the inner surface of pipes leads to an increase in the cost of 1 m 3 of water by up to 50%, and the cost of electricity for the production and sale of 1 m 3 of water is 30% higher than the average European level.
Thirdly: through holes formed in old rusted pipelines, water enters the ground, causing an increase in the level of groundwater, which in turn contributes to corrosion damage to the outer surface of the pipeline. It is obvious that rising groundwater levels due to leaks from pipelines also threaten the safety of utilities and buildings.
Fourth: losses of water during its transportation through leaky pipelines, amounting to tens of percent, lead to the fact that the consumer is forced to pay for water that he does not receive. Russia annually takes about 80 billion m 3 of water from open and underground sources for municipal, industrial and agricultural needs. If we accept losses in the amount of 30% of the volume of water supplied to the network (25 billion m 3), and the cost of 1 m 3 of water is 30 rubles, then the cost of annually lost water will be 225 billion rubles.
District heating pipelines
These pipelines supply hot water for heating and hot water supply systems.
Of approximately a third of a million km of heating networks (in single-pipe measurement), approximately a sixth are in need of replacement and repair. Obviously, in heating mains, in addition to the problems described in the story about pipelines for water supply (overgrowth and leaks), another important component is added - heat loss during the transportation of hot water from the heat source to its consumer.
The following truly depressing figures indicate the deterioration of modern heating networks:
- in some regions there are up to 400 accidents per 100 km of networks,
- Due to leaks in networks, over 70 million tons of standard fuel are lost without use, the total cost of which (at a cost of 1 t.u.t. 2100 rubles) is 147 billion rubles.
- According to the Association of Manufacturers and Consumers of Pipelines with Industrial Polymer Insulation, about 300 thousand accidents occur in heating networks every year in the country. With the average cost of eliminating one accident being 30 thousand rubles. annual costs may amount to 9 billion rubles.
- the durability of heating networks is 1.5-2 times lower than abroad, and does not exceed 12-15 years.
It is worth noting that the quality of heating mains is most relevant specifically for Russia, because We have the highest level of centralized heating supply (up to 80%).
The predominant method of laying heating networks in Russian Federation is laying in non-passable channels with mineral wool thermal insulation (80%). Channelless installation, carried out from factory-made structures using reinforced foam concrete insulation and bitumen-containing masses (bitumen-perlite, bitumen-vermiculite, bitumen-ceramsite), makes up 10% of the total length of heating networks.
Due to the moistening of the materials used during operation, the heat-protective properties of thermal insulation structures are sharply reduced, which leads to heat losses that are 2-3 times higher than the standard ones.
The total heat loss in district heating systems is about 20% of the supplied heat, which is 2 times higher than the same figure in advanced countries of Western Europe.
Water disposal (sewage) pipelines
More than 150,000 km of pipelines are used for drainage, of which more than 30% require replacement and repair. Worn out and old systems are depressurized, which creates a risk of contamination of water bodies. In addition, sewer networks are often laid next to water supply lines, and given that there are leaks in both of them, sewerage or soil contaminated by them is sucked in and enters water supply systems through aquifers. Worn underground pipelines are one of the main causes of intestinal infectious diseases, which have long been forgotten in developed countries!
We have reviewed the current deplorable situation. Question: "Who is to blame?" We’ll leave it for other authors and other publications, but here we’ll try to answer another eternal question:
What to do?
One of the main problems is that existing in Russia utility networks approximately 70% are made of steel pipes.
The main advantage of steel pipes is their strength. This is important when moving high-pressure media through pipelines. At the same time, in the housing and communal services sector, the strength properties of steel pipes are used by no more than 30%. Thus, the main advantage of steel pipelines turns out to be practically unnecessary, and the disadvantages (corrosion, and as a result through damage, losses of pumped liquid, groundwater suction, deterioration in the quality of transported water, overgrowing of the internal surface and a decrease in the internal cross-section, and as a consequence an increase in the energy spent on pumping water, etc.) take a lot of money.
In recent years, throughout the civilized world, steel pipes have been replaced by pipes made of polymer materials. This is not at all strange, because they are not subject to corrosion, and their service life is many times greater than the “life expectancy” of steel ones. This is clearly visible in Table 1.
Table 1. Standard service life of pipeline networks
The growth rate of the share of plastic pipes in developed countries is characteristic. In Europe, approximately 40 thousand km of plastic pipes are used per year. Their share in internal pipeline networks for new construction in industrialized countries is 20-40%, and in the most economically prosperous countries - even more (in Switzerland - 69.3%, in Finland - 50.8%, in Germany - 46, 2%). In the Netherlands specific gravity plastic pipelines in water supply systems exceed 40%. Currently in England, 99% of newly built water pipelines are polyethylene. Already in 1997, 1.9 billion m of such pipes were used in Western, Eastern and Central Europe. It is expected that the annual increase in the use of plastic pipes will be 6-8%.
I would like to dispel the typical misconception that plastic pipes are more expensive than steel pipes. Real calculations show that even in construction they are cheaper than steel pipes. According to the Moscow Research and Design Institute of Typology and Experimental Design (MNIITEP), the use of pipes made of polymer materials can reduce the cost of the sanitary section of a residential building by 23.5%, secondary school by 21.4%, children's preschool by 21.9%.
In the field of creating modern heating mains, the most relevant is the use of pipes in thermal insulation made of polyurethane foam and in a waterproof shell made of polyethylene or galvanized steel. Such pipelines can significantly reduce heat loss during its transportation, and also solve the problem of protecting the outer surface of steel pipes from corrosion.
To eliminate the possibility of internal corrosion of pipelines, the most optimal is an industrially manufactured heat pipeline design using pipes made of polymer materials that are not susceptible to corrosion and overgrowing of the internal surface with various deposits.
In particular, for hot water supply and heating systems, it is permissible to use pipes made of a random copolymer of propylene with ethylene (random copolymer - PPR-80), having a thermal insulating layer of polyurethane foam (PPU) and a waterproof coating (shell). When laying such pipes in the ground without channels, the waterproof shell is made of polyethylene pipe, with channel or open - made of galvanized steel. Another promising corrosion-resistant material for heat supply pipelines is cross-linked polyethylene, which is widely used in world practice for internal sanitary pipelines for hot water supply and heating.
To summarize, we can say that the problem of replacing old worn-out pipelines is indeed very large and serious, but it can be solved by using new materials and technologies.
Add to bookmarks
Moreover, they are still installed in most apartments. Steel pipes are characterized by low cost, but the cost of their installation is high. But even in this case, this option is much more economical than, for example,.
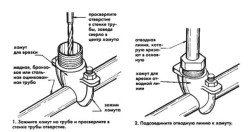
The branch line tie-in clamp allows you to connect to an existing pipeline without cutting it or inserting a tee
It is also important to note that for heating systems it is preferable to use pipes made of black steel, and for water supply it is better to choose galvanized ones. The main disadvantage of steel pipes is corrosion. It is completely impossible to prevent it. It can only be slowed down if zinc coating is used in the production of pipes (inside and outside).
When purchasing pipes for metal communications, pay attention to the method of their manufacture (this affects their service life). They can be either electric welded and used for water supply systems, heating systems and gas pipelines, or seamless. The fact is that with an equal internal diameter it is lower than, for example, copper or polymer. The reason lies in the inner surface, which is rough and, accordingly, causes turbulence in the fluid flow, thus complicating its progress.
Features of steel pipeline communications
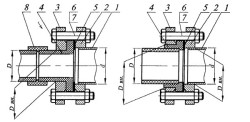
Installation of heating pipes when connecting shut-off/control valves or steel pipelines using flange connection, where 1 – steel pipe; 3 – steel flange according to GOST 12820-80 with a groove of internal diameter (2); 4 – collar bushing; 5 – gasket; 6 and 7 – fastening elements; 8 – coupling welded into a socket to a pipeline made of polymer material and a collar bushing.
Steel pipes can easily withstand hydraulic loads, and this does not affect their durability and, accordingly, does not shorten their service life. They have good thermal conductivity, and the low coefficient of expansion of the material when temperatures change allows it to be hidden in the wall. They are also perfect for creating radiant forms of water heating.
However, the disadvantages of metal steel communications are no less than the advantages. Of course, they are heavy and bulky, which makes them not so convenient to use. Installation of pipes is not possible without gas welding, which significantly increases its cost. On average, steel pipes in real life serve for more than 20 years.
They are operated in terrible conditions underground or in multi-storey buildings as various utility lines at a coolant temperature that is close to boiling and an internal pressure of more than 6 atm. And with water hammer it reaches 12-15 atmospheres. It is in such conditions that they are actually used, in a mode in which no metal-plastic or plastic pipe I couldn't stand even 15 minutes of work. This is the main advantage metal pipes.
In an ordinary city multi-story building, steel pipes serve either open or plastered in brick walls. In conditions in which the internal temperature is 6-7 atm., and the water temperature reaches 90 degrees, only pipes made of steel can work.
Due to their mechanical strength and low coefficient of thermal expansion, types of metal pipes currently have no competitors in the water supply and heat supply systems in urban multi-story buildings. But no one wants to work with such pipes, since they are straight (sometimes reaching 12 meters), heavy and difficult to transport. The most unpleasant thing when working with them is that they are installed using gas welding.
A few more benefits
It is worth mentioning the lifespan of steel pipes in Stalin-built houses, where they are used in the heating system at a temperature not exceeding 50-60 degrees. Heating systems that are equipped with cast iron radiators can easily last for more than a century. Although they can’t even do it, they still serve. There are cases where such heating systems were built in late XIX century and functioned perfectly until the mid-80s of the 20th century.
One more thing worth noting good property steel. It is difficult to overestimate - this is the lowest coefficient of thermal expansion among other pipes. So, for example, for copper it is 2 times greater, and for plastic it is 15-20 times greater. If we talk in simple language, then this is the stability of their sizes.
So, no other pipes should be hidden in the walls or floor, since they increase or decrease in size when the temperature changes (this is especially important if heating is being considered). And this already leads to a violation of the integrity of the coating in which they are mounted. Therefore, when using non-metallic pipes, compensating structures such as, for example, soft thermal insulation are used.
A steel pipe, like many metal pipes, is best suited for the construction of radiant (not to be confused with radiant) water heating systems. If we talk about disadvantages, the most important ones include a high level of corrosion, as well as damage of various types. All steel pipes used in heating rust very quickly and become clogged with various deposits. The best way protection is the use of galvanizing technology and laying pipes of larger diameter.
Perhaps the only and main disadvantage of using galvanizing is the impossibility of using antifreeze in this system, on which operation, that is, service life, depends. If we consider in more detail, zinc coating increases their resistance to corrosion, which can cause their service to deteriorate. This helps to extend the “life” and service life of metal structures by approximately several years.
Useful information about steel communications
There are several methods for galvanizing steel pipes: diffusion and hot. The hot-dip galvanizing method is a process where the entire surface is immersed directly in liquid zinc at a temperature of 450 degrees. This is a very labor-intensive process.
And diffuse coating is a process where the pipe is coated directly with zinc atoms at a temperature of 400 degrees. During this, zinc atoms penetrate into the intercrystal lattice of the heating pipe and form a fairly strong bond. This coating is carried out in special powder containers. That is why a galvanized steel pipe receives the necessary electrochemical protection. While other options for metal structures behave completely differently when galvanized, therefore they get a completely different result.
Installation of steel heating systems usually occurs in two ways: welding and twisting threads. The most common option is for heating, which occurs when using self-shielding wire. Its diameter ranges from 0.8 to 1.2 mm. In some cases, it is possible to use electrodes whose diameter can reach up to 3 mm.
But non-galvanized pipes are welded mainly with overlap. If there is, of course, a diameter of 25 mm. Enterprises sometimes use butt joints for pipes of this diameter. The main difficulties are caused by welding metal heating pipes that are under pressure, because they are almost always located close to the walls of the building. During installation heating system special requirements apply to weld seam, the outer surface of which should be cooked evenly without any cuts, cracks or sagging.
Steel pipes have a good 50-year history of use, significant advantages and look quite good compared to new ones modern technologies. But still, the use of metal pipes slightly lost its relevance when polymer pipes began to be actively used in heating systems.